Discover the various diagnostic tests used to identify malaria. This guide offers detailed insights into the methods, their accuracy, and their applications in different settings.
Blog
Malaria Diagnostic Tests: Methods, Accuracy & Use Cases
Malaria remains a significant public health challenge in many parts of the world. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and control of the disease. Various diagnostic tests are available, each with its own advantages and limitations. This comprehensive guide explores the different diagnostic tests for malaria, detailing their methods, accuracy, and appropriate applications.
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, with Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae being the species that infect humans. The disease is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, and in severe cases, anemia, jaundice, and organ failure. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and preventing complications.
Microscopy remains the gold standard for malaria diagnosis due to its ability to identify the species and quantify the level of parasitemia.
Light microscopy involves examining stained blood smears under a microscope. The two types of blood smears are thick and thin smears. Thick smears are more sensitive for detecting low levels of parasitemia, while thin smears help in species identification.
Giemsa stain is commonly used for staining blood smears. It highlights the parasites within red blood cells, allowing for visualization and identification.
Advantages of microscopy include its ability to provide detailed information about the parasite species and density. However, it requires skilled personnel, high-quality reagents, and proper maintenance of microscopes.
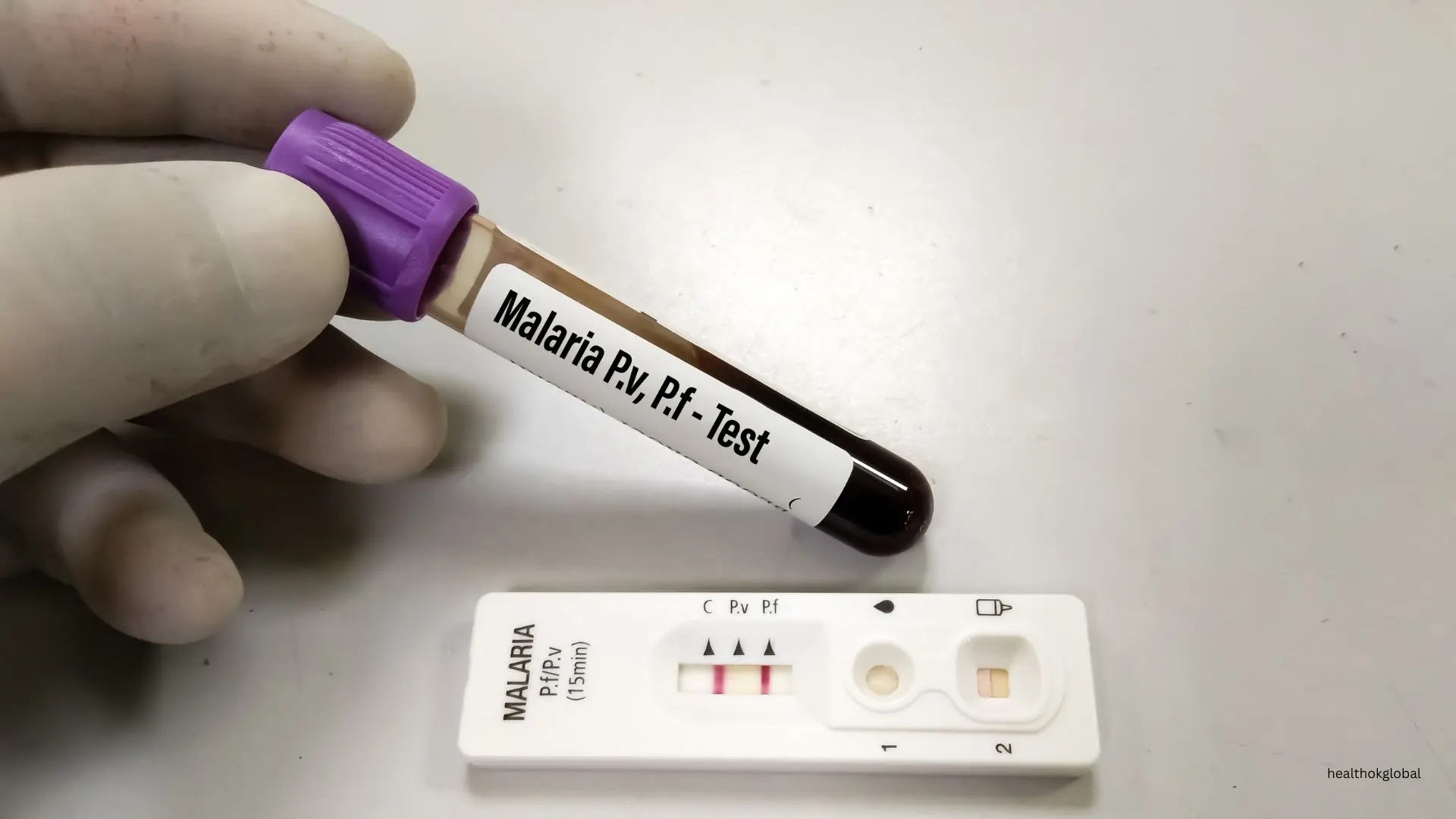
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) provide a quick and easy method for diagnosing malaria, especially in remote and resource-limited settings.
RDTs work by detecting specific antigens produced by malaria parasites. A drop of blood is applied to the test strip, which contains antibodies that bind to the antigens. A visible line indicates a positive result.
Different RDTs target different antigens, such as histidine-rich protein 2 (HRP2) for P. falciparum and Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) for all species.
RDTs are user-friendly, provide rapid results, and do not require extensive training or equipment. However, their accuracy can be affected by factors such as antigen variability, cross-reactivity, and storage conditions.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a molecular technique that amplifies the DNA of malaria parasites, allowing for highly sensitive and specific detection.
PCR involves extracting DNA from a blood sample and using specific primers to amplify parasite DNA. The amplified DNA is then detected and analyzed.
Different types of PCR include conventional PCR, real-time PCR, and nested PCR. Each type varies in its methodology and application.
PCR is highly sensitive and can detect low levels of parasitemia. It can also identify mixed infections and drug resistance markers. However, it requires specialized equipment, trained personnel, and is more expensive and time-consuming compared to other methods.
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is a molecular technique that allows for rapid and sensitive detection of malaria parasites.
LAMP amplifies DNA at a constant temperature, eliminating the need for thermal cycling. It uses a set of primers and a DNA polymerase to produce large amounts of DNA from a small sample.
LAMP is faster and simpler than PCR, making it suitable for field settings. It provides results in less than an hour and does not require sophisticated equipment. However, it still requires some level of technical expertise and proper handling to avoid contamination.
Serological tests detect antibodies produced in response to malaria infection. These tests are useful for epidemiological studies and identifying past infections.
Serological tests detect specific antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to malaria parasites. Common methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA).
Serological tests are useful for detecting past infections and for epidemiological surveillance. However, they are not suitable for diagnosing acute infections because antibodies can persist long after the infection has been cleared.
Several other methods are being developed and tested for malaria diagnosis, including biosensors, microfluidic devices, and next-generation sequencing.
Biosensors use biological molecules to detect malaria antigens or DNA. These devices offer the potential for rapid, sensitive, and portable testing.
Microfluidic devices manipulate small volumes of fluids to detect malaria parasites. These devices are being developed to provide rapid and accurate diagnosis at the point of care.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) can provide comprehensive data on the genetic makeup of malaria parasites, including drug resistance markers. While still in the research phase, NGS has the potential to revolutionize malaria diagnostics.
Each diagnostic method has its own strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different contexts and purposes.
Microscopy and PCR are highly specific, while RDTs and LAMP offer a good balance of sensitivity and simplicity. Serological tests are less specific for acute infections but valuable for epidemiological studies.
Microscopy and RDTs are cost-effective and suitable for low-resource settings. PCR and NGS are more expensive and require specialized equipment, making them suitable for reference laboratories.
RDTs and LAMP provide rapid results, while microscopy and PCR require more time for sample preparation and analysis. NGS offers detailed information but has the longest turnaround time.
The choice of diagnostic test depends on various factors, including the setting, available resources, and the purpose of the diagnosis.
In clinical settings, rapid and accurate diagnosis is essential for timely treatment. RDTs and microscopy are commonly used in these settings due to their quick turnaround time and reliability.
In field settings, where resources are limited, RDTs and LAMP are preferred due to their ease of use and minimal equipment requirements.
For research and surveillance, PCR and NGS provide detailed information on parasite genetics and epidemiology, making them valuable tools for tracking drug resistance and infection patterns.
Accurate and timely diagnosis of malaria is crucial for effective treatment and control of the disease. Each diagnostic method has its own strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different contexts and purposes. By understanding the various diagnostic tests available, healthcare providers can choose the most appropriate method for their specific needs, ensuring the best outcomes for patients and communities.
HealthOK Global's dedicated care team provides essential healthcare assistance for the elderly in India, ensuring they receive comprehensive support in the comfort of their homes. From routine medical check-ups and medication management to personalized nursing care and emergency response services, our expert caregivers are committed to enhancing the quality of life for seniors. With our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline, you can reach us anytime at +91-8047190955 (India) or +1-888-462-1804 (USA) to ensure your loved ones receive the best possible care.
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, with Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae being the species that infect humans. The disease is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, and in severe cases, anemia, jaundice, and organ failure. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and preventing complications.
Microscopy remains the gold standard for malaria diagnosis due to its ability to identify the species and quantify the level of parasitemia.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a molecular technique that amplifies the DNA of malaria parasites, allowing for highly sensitive and specific detection.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





