The homocysteine test measures the level of homocysteine in the blood, which can indicate various health conditions.
Blog
The Homocysteine Test: Importance and Procedure
The homocysteine test measures the level of homocysteine in the blood, which can indicate various health conditions. Elevated homocysteine levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and other health issues. This article delves into the importance of the homocysteine test, the procedure involved, and how to interpret the results for better health management.
Homocysteine is an amino acid produced during the metabolism of methionine, an essential amino acid found in dietary proteins. Normally, homocysteine is converted into other beneficial substances with the help of vitamins B6, B12, and folate. However, if this process is disrupted, homocysteine levels can rise, leading to potential health risks.
The homocysteine test is crucial for several reasons:
High homocysteine levels are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. Monitoring these levels can help assess cardiovascular risk.
Elevated homocysteine can indicate deficiencies in vitamins B6, B12, and folate, which are essential for its metabolism. Identifying these deficiencies can guide dietary and supplementation strategies.
Abnormal homocysteine levels are associated with neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and cognitive decline. Monitoring these levels can be part of a broader strategy for managing neurological health.
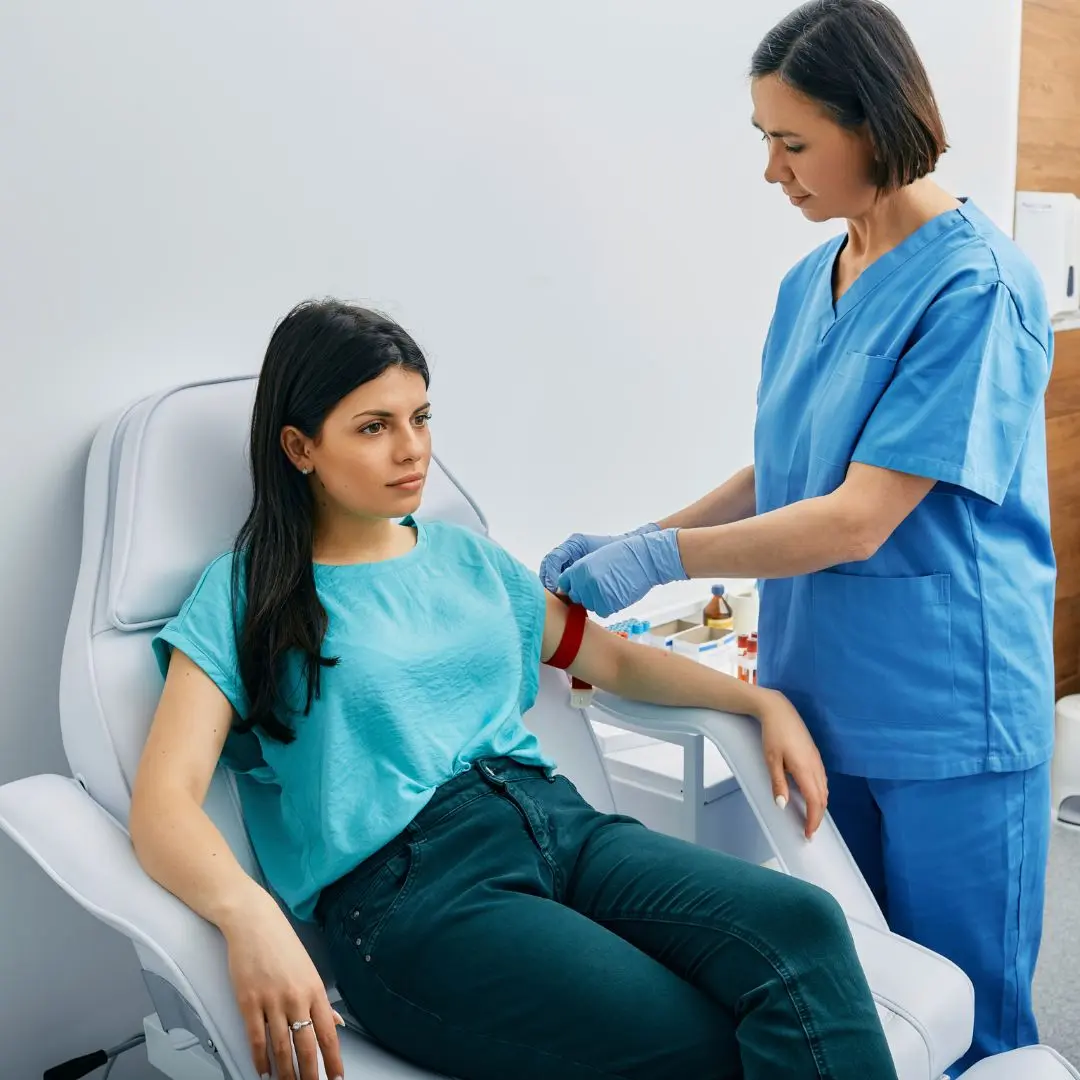
The homocysteine test involves a simple blood draw, usually performed in a clinical setting. Here is an overview of the procedure:
Patients may be advised to fast for 8-12 hours before the test to ensure accurate results. They should also inform their healthcare provider of any medications or supplements they are taking.
A healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein, typically in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The laboratory measures the homocysteine levels in the blood. Results are usually available within a few days, depending on the laboratory's processing time.
Understanding the results of the homocysteine test is vital for health management:
The normal range for homocysteine levels is typically between 5 and 15 micromoles per liter (µmol/L). However, reference ranges can vary slightly between laboratories.
Homocysteine levels above the normal range may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, vitamin deficiencies, or other health issues. Elevated levels require further investigation and management.
Low homocysteine levels are rare but can occur and may indicate an overactive thyroid or other metabolic conditions. Further testing may be required to determine the underlying cause.
Several factors can influence homocysteine levels, including:
A diet low in vitamins B6, B12, and folate can lead to elevated homocysteine levels. Ensuring adequate intake of these vitamins through diet or supplements is crucial.
Genetic mutations, such as the MTHFR mutation, can impair homocysteine metabolism, leading to higher levels.
Certain medications, such as methotrexate and antiepileptic drugs, can affect homocysteine levels. Patients should discuss their medications with their healthcare provider.
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can elevate homocysteine levels. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage these levels.
Managing elevated homocysteine levels involves addressing underlying causes and making lifestyle changes:
Increasing intake of foods rich in vitamins B6, B12, and folate, such as leafy greens, legumes, and fortified cereals, can help lower homocysteine levels.
In cases of significant deficiencies, supplements may be necessary to restore normal homocysteine levels. Patients should follow their healthcare provider's recommendations.
Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity can positively impact homocysteine levels and overall health.
Patients should discuss any medications that may affect homocysteine levels with their healthcare provider. Adjustments or alternative treatments may be necessary.
Regular monitoring of homocysteine levels can be beneficial for individuals at risk of cardiovascular diseases or with a family history of health conditions associated with elevated homocysteine. It is particularly important for:
Those with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or a history of heart disease should consider regular homocysteine testing.
Individuals diagnosed with deficiencies in vitamins B6, B12, or folate should monitor their homocysteine levels to ensure proper management.
Those with known genetic mutations affecting homocysteine metabolism may benefit from regular testing and proactive management.
The homocysteine test is an important tool for assessing cardiovascular risk, identifying nutritional deficiencies, and managing various health conditions. By understanding the significance of homocysteine levels and taking proactive steps to manage them, individuals can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of serious diseases. Regular testing, combined with a healthy lifestyle and appropriate medical care, is key to maintaining optimal health.
Homocysteine is an amino acid produced during the metabolism of methionine, an essential amino acid found in dietary proteins. Normally, homocysteine is converted into other beneficial substances with the help of vitamins B6, B12, and folate. However, if this process is disrupted, homocysteine levels can rise, leading to potential health risks.
Regular monitoring of homocysteine levels can be beneficial for individuals at risk of cardiovascular diseases or with a family history of health conditions associated with elevated homocysteine. It is particularly important for:
Managing elevated homocysteine levels involves addressing underlying causes and making lifestyle changes:
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.