Interferential Therapy (IFT) is a form of electrical stimulation used in physiotherapy to treat pain and promote healing in soft tissues.
Blog
IFT Physiotherapy: A Comprehensive Guide to Interferential Therapy
Interferential Therapy (IFT) is a form of electrical stimulation used in physiotherapy to treat pain and promote healing in soft tissues. IFT employs low-frequency electrical currents that penetrate deep into the tissues, providing pain relief and stimulating the healing process. This therapy is particularly effective for conditions involving chronic pain, muscle spasms, and inflammation.
IFT works by delivering electrical currents through the skin to the underlying tissues. These currents are set at two slightly different frequencies, which intersect to create a low-frequency stimulation deep within the tissues. This low-frequency stimulation is believed to have several therapeutic effects, including pain relief, reduction of inflammation, and promotion of tissue healing.
IFT stimulates the production of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers, which help reduce the sensation of pain.
The electrical currents enhance blood flow to the affected area, which helps reduce inflammation and promotes healing.
IFT can help relax muscles and reduce muscle spasms, providing relief from pain and improving mobility.
IFT physiotherapy offers several benefits for patients suffering from various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. These benefits include pain relief, improved mobility, and faster recovery.
IFT is highly effective in managing both acute and chronic pain. It provides immediate pain relief and can reduce the need for pain medications.
IFT is a non-invasive treatment option that does not require surgery or injections. This makes it a safe and suitable option for many patients.
By improving circulation and reducing muscle spasms, IFT helps decrease inflammation in the affected area.
The increased blood flow and stimulation of tissue repair processes promote faster healing of injured tissues.
IFT can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including back pain, arthritis, sports injuries, and post-surgical pain.
IFT physiotherapy is used to treat a variety of conditions that cause pain and inflammation. Some of the most common conditions include:
IFT is effective in relieving chronic back pain caused by conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and muscle strains.
Patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can benefit from IFT as it helps reduce joint pain and inflammation.
Athletes suffering from injuries such as sprains, strains, and tendonitis can use IFT to manage pain and accelerate recovery.
IFT can be used as part of post-operative rehabilitation to reduce pain and promote healing after surgery.
Conditions like sciatica and peripheral neuropathy, which cause nerve pain, can be effectively managed with IFT.
The IFT procedure involves a few simple steps and is typically performed by a trained physiotherapist. Here’s what to expect during an IFT session:
The physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
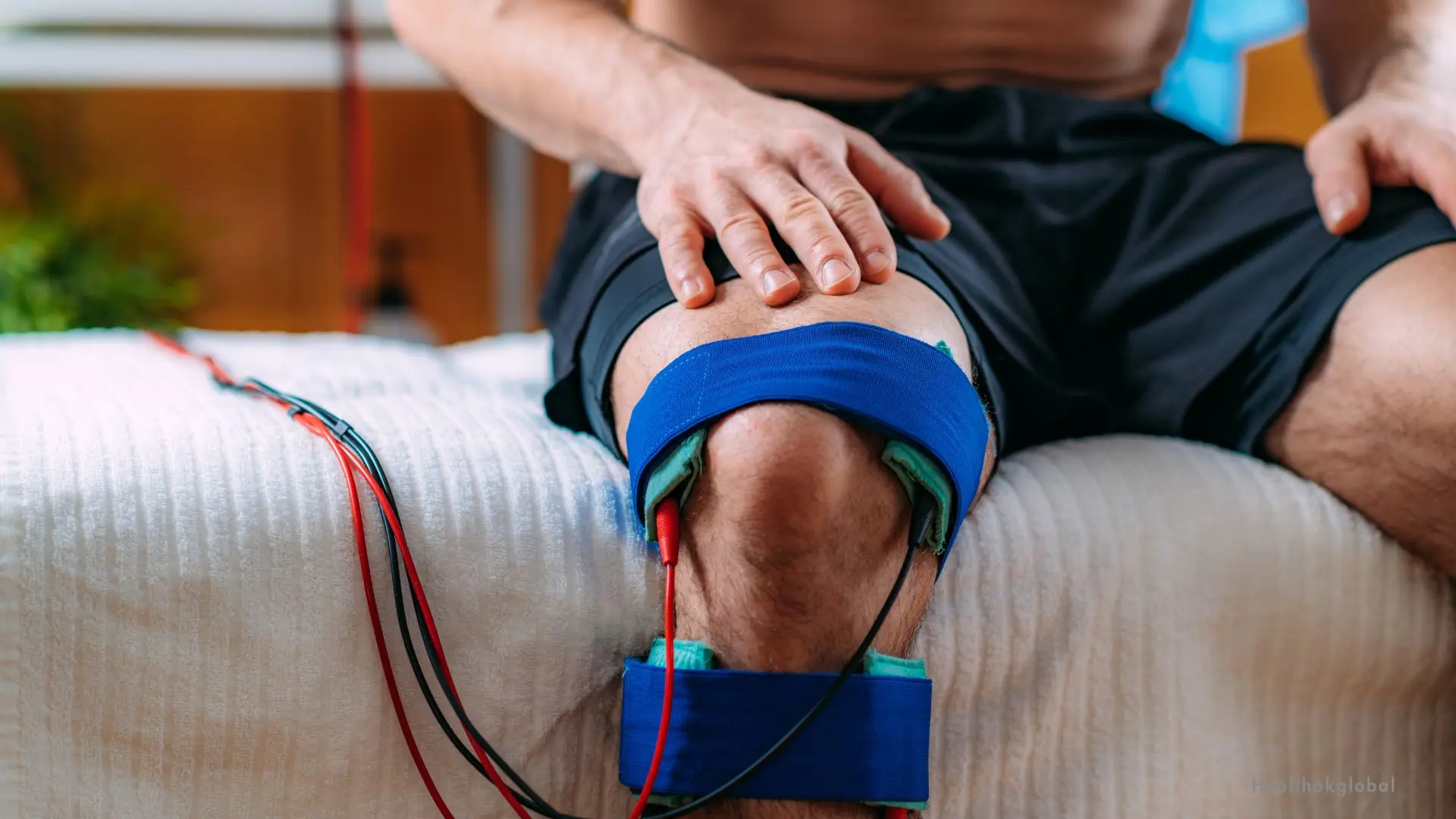
Electrodes are placed on the skin around the area of pain or injury. The placement of electrodes is crucial for effective treatment.
The therapist will set the appropriate frequency and intensity of the electrical currents based on the patient’s condition and tolerance.
The IFT machine delivers the electrical currents for a specified duration, usually between 15 to 30 minutes. The patient may feel a tingling sensation during the treatment.
After the session, the therapist may provide additional exercises or advice on how to manage the condition at home.
While IFT is generally safe for most patients, there are certain contraindications and precautions that need to be considered. Patients should inform their physiotherapist of any underlying health conditions or concerns.
1. Pacemakers: Patients with pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices should avoid IFT. 2. Pregnancy: IFT is not recommended for pregnant women, especially in the abdominal and pelvic regions. 3. Infections or Open Wounds: IFT should not be used over areas with active infections or open wounds. 4. Malignancies: Patients with cancer should avoid IFT in the affected area without medical clearance.
1. Skin Sensitivity: Patients with sensitive skin or allergies should inform their therapist to prevent skin irritation. 2. Heart Conditions: Individuals with heart conditions should use IFT with caution and under medical supervision. 3. Children: IFT is generally safe for children but should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
IFT physiotherapy can be combined with other treatment modalities to enhance its effectiveness and provide comprehensive care. Combining therapies can address different aspects of the condition and promote overall recovery.
Techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and soft tissue manipulation can complement IFT by improving flexibility and reducing muscle tension.
A tailored exercise program can strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and support the benefits of IFT.
Water-based exercises and treatments can provide additional pain relief and support rehabilitation efforts.
Providing patients with education on posture, ergonomics, and lifestyle changes can help prevent future injuries and manage chronic conditions effectively.
Interferential Therapy (IFT) is a valuable tool in physiotherapy for managing pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing. Its non-invasive nature and effectiveness make it a popular choice for treating a wide range of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. By understanding the benefits, procedure, and safety considerations of IFT, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options. Combining IFT with other therapies can further enhance recovery and improve quality of life. Investing in IFT physiotherapy can lead to significant improvements in pain management and overall health, enabling individuals to lead more active and fulfilling lives.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights on nutrition, meal planning, and healthy eating habits. Contact our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline at +91-8047190955 for assistance.
IFT works by delivering electrical currents through the skin to the underlying tissues. These currents are set at two slightly different frequencies, which intersect to create a low-frequency stimulation deep within the tissues. This low-frequency stimulation is believed to have several therapeutic effects, including pain relief, reduction of inflammation, and promotion of tissue healing.
IFT physiotherapy offers several benefits for patients suffering from various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. These benefits include pain relief, improved mobility, and faster recovery.
While IFT is generally safe for most patients, there are certain contraindications and precautions that need to be considered. Patients should inform their physiotherapist of any underlying health conditions or concerns.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





