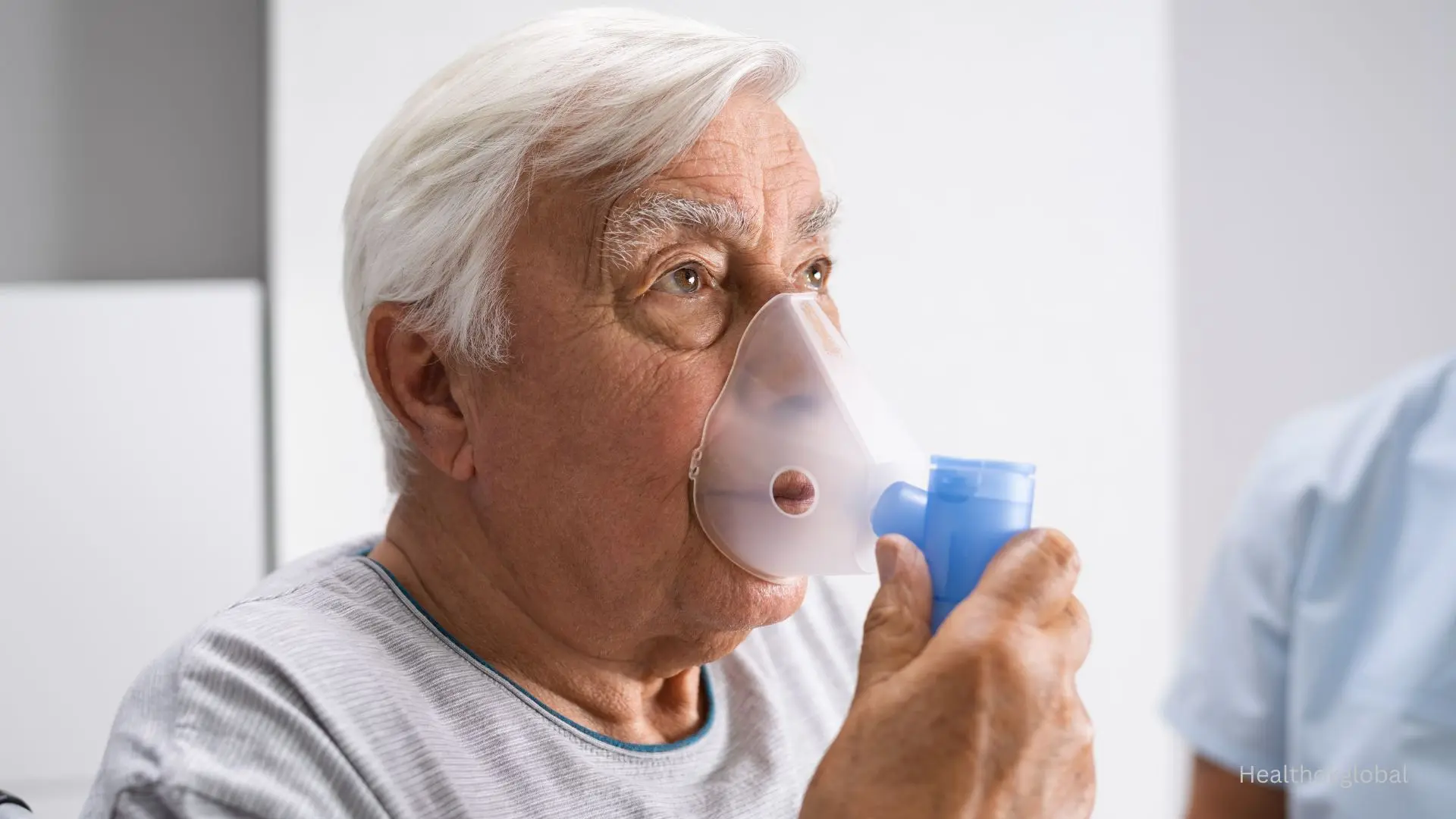
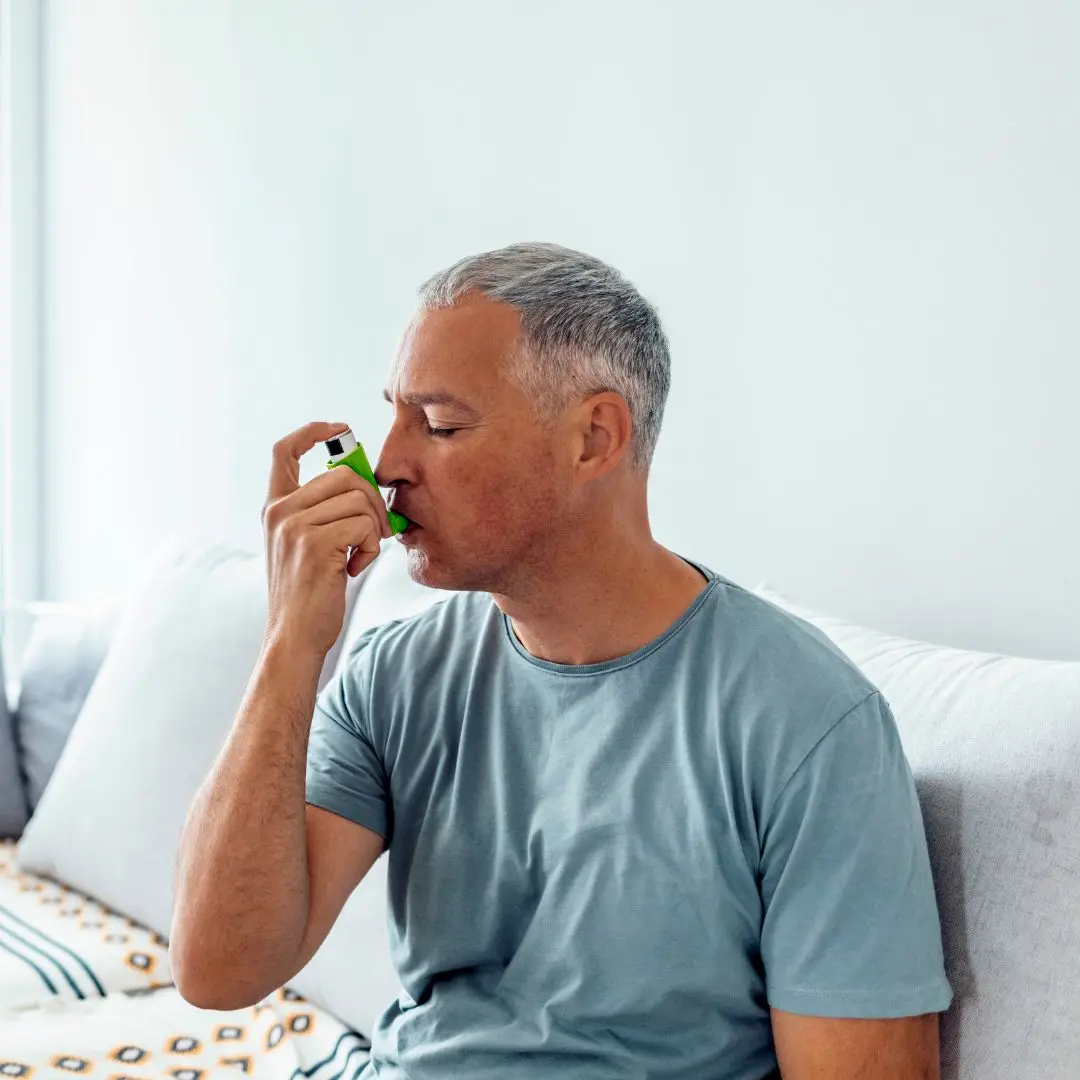
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and chest tightness.

Blog
Is Asthma a Communicable Disease? Exploring the Contagiousness of Asthma
Asthma is a widespread chronic respiratory disorder affecting over 262 million people globally, as reported by the World Health Organization. While symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and breathlessness are well-known, there’s still confusion among the public about whether asthma is contagious. This blog explores that question in detail, explaining why asthma is classified as a non-communicable disease, and how it differs from infectious illnesses.
Communicable diseases are illnesses caused by infectious agents—bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites—that are transmitted from one individual to another, either directly (e.g., through bodily fluids) or indirectly (e.g., via contaminated surfaces or air). Examples include the flu, COVID-19, tuberculosis, and malaria. These diseases often require public health interventions to control outbreaks.
Unlike contagious diseases, asthma is not caused by infectious agents. It is a chronic, non-communicable disease (NCD), meaning it cannot be passed from person to person. Instead, it arises due to a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle-related factors. According to the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), asthma is one of the most common NCDs worldwide. Although asthma symptoms may be triggered by respiratory infections, the condition itself remains non-infectious.
Understanding what causes asthma is essential to separating myth from fact. Here are some scientifically recognized risk factors:
Individuals with a family history of asthma or allergies are more likely to develop the condition.
Exposure to indoor and outdoor allergens, pollution, and smoking can provoke inflammation in sensitive airways.
Severe respiratory infections early in life can affect lung development and immune response.
Lack of essential nutrients like vitamin D, magnesium, or antioxidants can increase inflammation. Explore the role of personalized nutrition plans in reducing asthma risk.
Triggers are not the cause of asthma but are stimuli that worsen the symptoms. Recognizing and avoiding them is vital for asthma control:
These include pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander, and cockroach droppings.
Cold air, sudden temperature changes, and high humidity can constrict airways.
Physical exertion and emotional stress are common but manageable triggers.
Viruses like the flu or common cold can provoke severe flare-ups, especially in children.
Acid reflux and constipation can exacerbate asthma. Try acupressure for constipation to improve gut-lung balance.
Asthma is manageable with a combination of preventive care, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s how to control it effectively:
Short-acting beta agonists (like albuterol) relieve symptoms, while corticosteroids reduce airway inflammation.
Use air purifiers, wear masks in high-pollution areas, and avoid known irritants.
Work with your doctor to create a personalized plan, including what to do during an asthma attack.
Healthy weight management, hydration, and balanced nutrition significantly improve asthma control.
Misinformation often leads to fear and stigma. Let’s clarify some common misconceptions:
Fact: Asthma cannot be spread from one person to another. It is a chronic, non-communicable disease.
Fact: With proper management, most people with asthma can safely enjoy physical activity.
Fact: Asthma can develop at any age and often persists into adulthood.
Asthma education plays a crucial role in effective disease management. Community programs, school interventions, and digital health platforms are empowering patients and caregivers. With the rise of online tools and customized health content, individuals are now more equipped than ever to manage asthma through awareness, diet, and lifestyle strategies.
Ritika, a 19-year-old college student, used to suffer weekly asthma attacks triggered by stress and cold air. Through regular consultation with her pulmonologist, implementing dietary changes using personalized nutrition plans, and using an asthma tracker app, she reduced her attacks to less than one per quarter. Her story reflects the power of awareness and integrated care.
No. Unlike communicable diseases, asthma cannot be transmitted via respiratory droplets.
Viral infections can trigger asthma symptoms but do not cause the condition itself.
Yes. With proper management and lifestyle changes, individuals with asthma can lead full, active lives.
Asthma is chronic and often linked to allergies, while bronchitis is typically a short-term infection caused by a virus or bacteria.
Asthma is a non-communicable respiratory condition that requires education, awareness, and personalized management to live symptom-free. It’s not contagious, but it is widespread and often misunderstood. By distinguishing asthma from infectious diseases and correcting public misconceptions, we create a more supportive, stigma-free environment for millions living with asthma.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights into disease prevention and diagnostic advancements. Call our 24x7 healthcare helpline at +91-8047190955.
Unlike contagious diseases, asthma is not caused by infectious agents. It is a chronic, non-communicable disease (NCD), meaning it cannot be passed from person to person. Instead, it arises due to a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle-related factors. According to the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), asthma is one of the most common NCDs worldwide. Although asthma symptoms may be triggered by respiratory infections, the condition itself remains non-infectious.
No. Unlike communicable diseases, asthma cannot be transmitted via respiratory droplets.
Viral infections can trigger asthma symptoms but do not cause the condition itself.
Yes. With proper management and lifestyle changes, individuals with asthma can lead full, active lives.
Asthma is chronic and often linked to allergies, while bronchitis is typically a short-term infection caused by a virus or bacteria.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.