Introduction to Diabetes
Understanding Diabetes
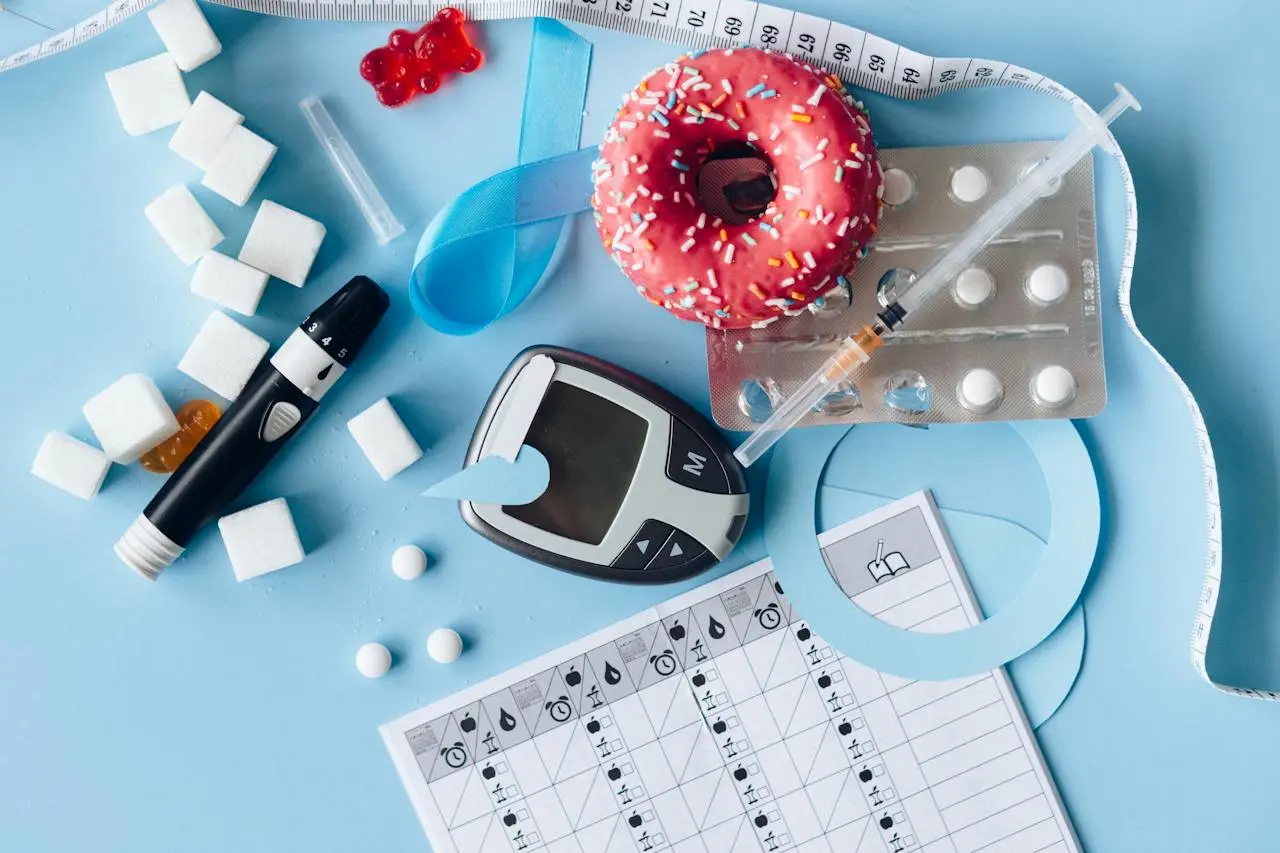
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to use the insulin it produces effectively. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose to enter cells and be used as energy. When this process is disrupted, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to various health complications.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: This occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 diabetes: This is the most common form of diabetes, usually developing in adulthood. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body is unable to effectively. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity contribute to the development type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after giving birth. However, women who develop gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of diabetes is not fully understood. However, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the condition. These include family history, obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, high blood pressure, and ethnicity (some ethnic groups are at higher risk).
Recognizing Diabetes Symptoms
Early Warning Signs
It's important to be aware of the early warning signs of diabetes, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications. Some early symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Common Symptoms
As diabetes progresses, more noticeable symptoms may appear, such as slow-healing wounds, frequent infections, tingling or numbness in the hands or feet, and recurring skin infections. These symptoms indicate that blood sugar levels are consistently high and warrant medical attention.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
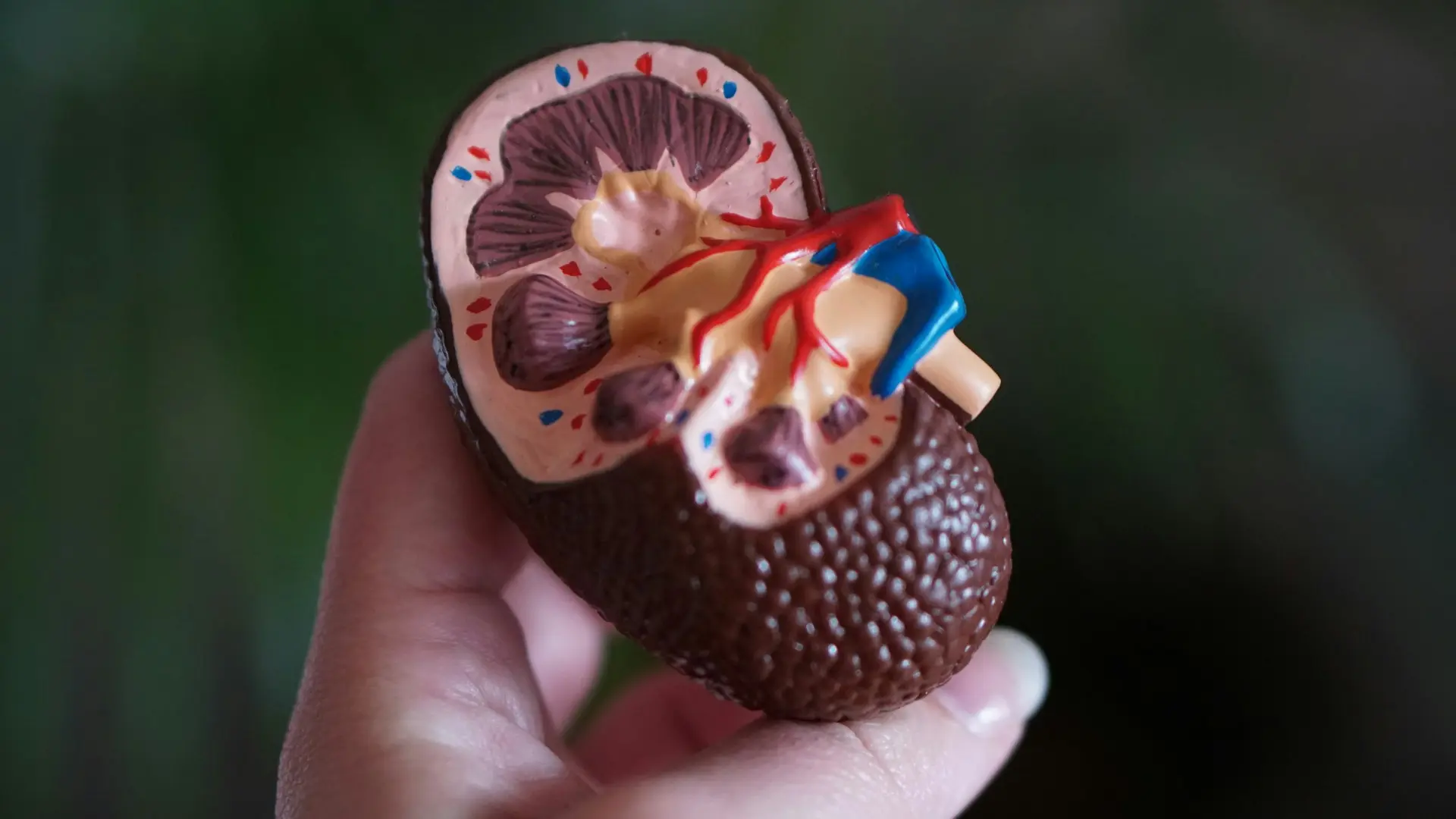
Timely diagnosis is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision loss. Therefore, it's important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any symptoms or have any risk factors.
Diabetes Complications
Long-term Health Risks
Diabetes can have significant long-term health risks. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and eye problems. Proper management of diabetes is essential to reduce these risks.
Impact on Quality of Life
Living with diabetes can impact a person's quality of life. Constant monitoring of blood sugar levels, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications can be challenging and may lead tofeelings of frustration or anxiety. However, with proper support and guidance, individuals with diabetes can maintain a good quality of life.
Importance of Proper Management
Managing diabetes effectively is essential for preventing complications and maintaining overall health. This involves a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By following a comprehensive diabetes management plan, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and lead a fulfilling life
Diabetes Prevention and Diagnosis
Preventing Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, type 2 diabetes can often be delayed or prevented altogether by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Making healthy food choices, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes
Balancing Diet and Physical Activity
A balanced diet and regular physical activity play a crucial role in preventing and managing diabetes. Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, along with strength training exercises, is recommended for managing diabetes.
Risk Reduction Strategies
In addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, certain risk reduction strategies can help prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. These include managing stress levels, getting adequate sleep, and reducing the consumption of sugary beverages and processed foods.
Diabetes Screening and Diagnosis
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are essential for diagnosing diabetes and monitoring its progression. Healthcare professionals can perform blood tests to measure fasting blood sugar levels, oral glucose tolerance tests, or glycated hemoglobin (A1C) tests to assess blood sugar control over the past few months.
Diagnostic Tests and Methods
Various diagnostic tests and methods help diagnose diabetes. These include measuring blood glucose levels, analyzing urine for glucose and ketones, and conducting genetic testing in certain cases. A healthcare professional will determine the most appropriate diagnostic method based on an individual's symptoms and risk factors.
Seeking Medical Help
If you experience any diabetes symptoms or have risk factors associated with the condition, it's important to seek medical help. Healthcare professionals can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan based on individual needs.
Diabetes Management Options
Medication and Insulin
Managing diabetes often involves medication and insulin therapy. Medications such as metformin or insulin injections help regulate blood sugar levels. The type and dosage of medication will depend on the type of diabetes and individual factors
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are fundamental in diabetes management. These include adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress levels. These lifestyle changes contribute to better blood sugar control and overall well-being
Role of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes. It allows for adjustments in medication, diet, and physical activity to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Blood glucose meters, continuous glucose monitors, and insulin pumps assist in monitoring blood sugar levels accurately.
Diet and Nutrition for Diabetic Patients
Healthy Eating Principles
Adopting healthy eating principles is essential for individuals with diabetes. A balanced diet should include a variety of food groups, including carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The focus should be on portion control, moderation, and mindful eating
Understanding Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins
Understanding carbohydrates, fats, and proteins is crucial for managing diabetes. Carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels the most, so it's important to choose complex carbs, such as whole grains, and monitor portion sizes. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and nuts, are important for heart health. Proteins are essential for muscle repair and should be included in every meal.
Portion Control and Meal Planning
Portion control plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Balancing the amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats consumed in each meal is important. Meal planning and mindful eating help individuals with diabetes make healthier choices and maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. It helps control blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, reduces the risk of heart disease, and promotes overall physical and mental well-being
Types of Exercises for Diabetic Patients
A well-rounded exercise routine should include aerobic activities, resistance training, and flexibility and balance exercises. Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling, help lower blood sugar levels. Resistance training improves insulin sensitivity, while flexibility and balance exercises promote mobility and reduce the risk of falls.
Creating an Exercise Routine
When creating an exercise routine, it's important to set realistic goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the activities. Safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate footwear and monitoring blood sugar levels before and after exercise, should be followed. Finding personal motivations, such as exercising with a friend or listening to motivational music, can help individuals stay committed to their routine
Emotional Well-being and Diabetes
Emotional Impact of Diabetes
Managing diabetes can have a significant emotional impact on individuals. The constant need to monitor blood sugar levels, adhere to medication routines, and make lifestyle modifications can cause feelings of stress, anxiety, or even depression. Additionally, diabetes management can affect personal relationships and social activities.
Coping with the Emotional Challenges
Coping with the emotional challenges of diabetes requires adopting healthy coping strategies. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or practicing mindfulness and meditation, can help reduce stress levels. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can also provide a valuable outlet for emotional support
Importance of Support Systems
Having a strong support system is essential for individuals managing diabetes. Family, friends, healthcare professionals, and diabetes support groups can offer encouragement and practicaladvice during challenging times. Open communication and sharing experiences with others who understand the daily struggles of diabetes can alleviate feelings of isolation.
Summary and FAQs
Summary of Key Points
Understanding Diabetes and its Types: Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or doesn't use it effectively. The three main types are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes
Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies: Preventing type 2 diabetes involves healthy lifestyle choices, while diagnosis and management require regular check-ups, medication or insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and blood sugar monitoring.
Importance of Healthy Diet, Exercise, and Emotional Well-being: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and emotional well-being are crucial aspects of managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications.