Developing an effective nursing care plan for patients with pneumonia involves thorough assessment, diagnosis, and intervention. This guide provides essential information on creating and implementing a nursing care plan for pneumonia.
Blog
Comprehensive Guide to Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia
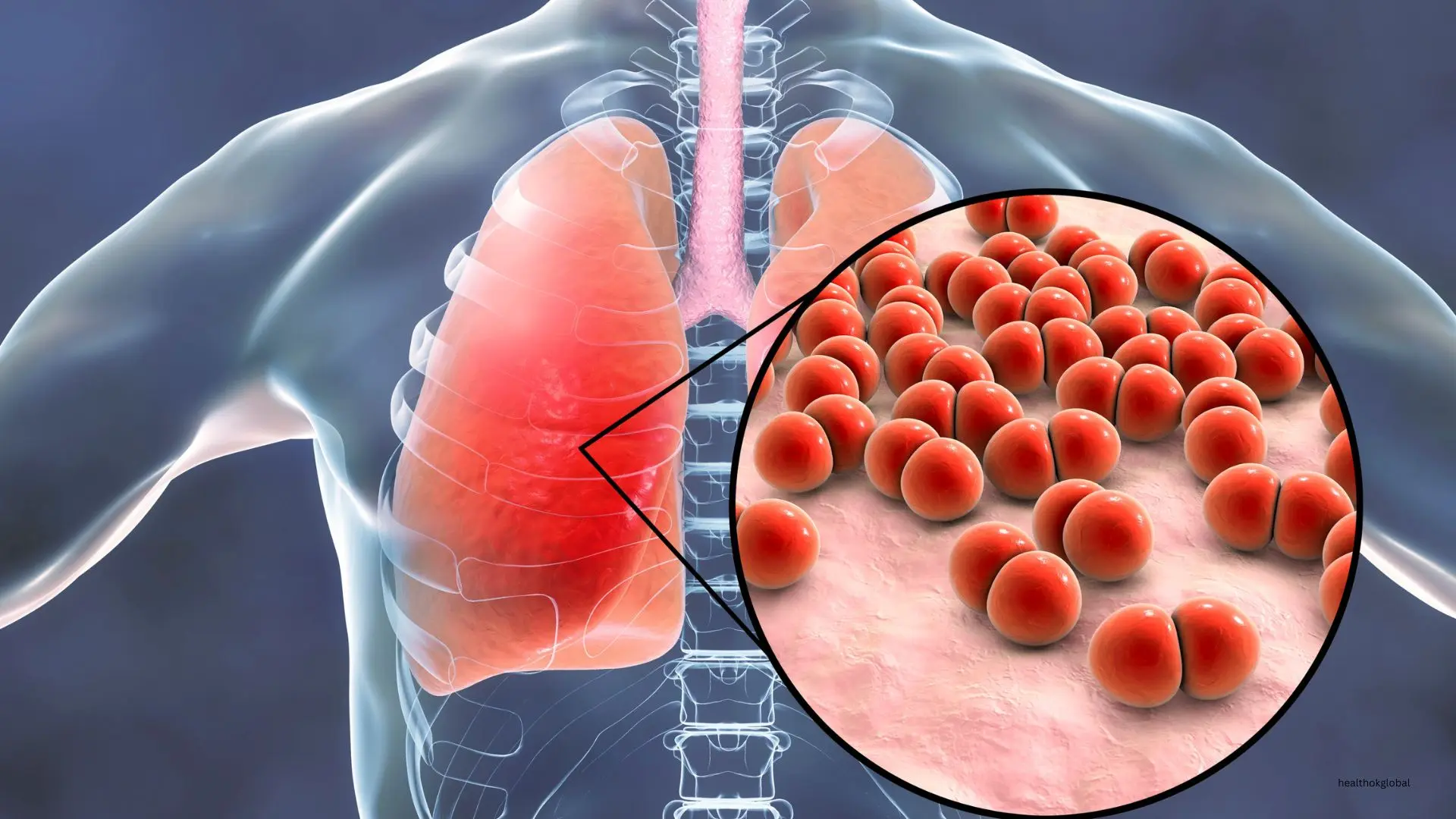
Developing an effective nursing care plan for patients with pneumonia involves thorough assessment, diagnosis, and intervention. Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. This comprehensive guide provides essential information on creating and implementing a nursing care plan for pneumonia, ensuring patient recovery and comfort.
Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and is classified based on the causative agent and the location where the infection was acquired (community-acquired, hospital-acquired, or healthcare-associated). The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, infants, and those with chronic illnesses.
The first step in creating a nursing care plan for pneumonia is a comprehensive assessment. Key aspects of the assessment include:
Gathering a detailed patient history, including the onset, duration, and characteristics of symptoms such as cough, sputum production, fever, and chest pain.
Conducting a thorough physical examination to assess respiratory status, including lung auscultation to detect abnormal breath sounds, and evaluating oxygen saturation levels.
Ordering relevant diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays, sputum cultures, blood tests, and pulse oximetry, to confirm the diagnosis and identify the causative agent.
Analyzing the characteristics of symptoms, such as the type of cough (productive or non-productive), the color and consistency of sputum, and the presence of accompanying symptoms like dyspnea or pleuritic chest pain.
Based on the assessment, the following nursing diagnoses may be identified for a patient with pneumonia:
Related to increased secretions and inflammation, as evidenced by abnormal breath sounds and difficulty expectorating sputum.
Related to alveolar-capillary membrane changes, as evidenced by hypoxemia and dyspnea.
Related to infection, as evidenced by elevated body temperature.
Related to pleuritic chest pain, as evidenced by the patient's report of pain and guarded breathing.
Related to compromised immune response or exposure to pathogens.
Nursing interventions for managing pneumonia focus on relieving symptoms, addressing the underlying cause, and preventing complications. Key interventions include:
Encouraging deep breathing exercises, coughing, and using incentive spirometry to maintain airway patency and clear secretions.
Administering supplemental oxygen as prescribed to maintain adequate oxygen saturation levels and relieve dyspnea.
Administering prescribed medications, such as antibiotics, antivirals, antipyretics, and bronchodilators, and monitoring for side effects.
Encouraging oral fluid intake if tolerated, and administering intravenous fluids if necessary to maintain hydration and help thin secretions.
Providing small, frequent meals that are high in protein and calories to support the patient's energy needs and immune function.
Implementing comfort measures such as positioning the patient to facilitate breathing, using a cool mist humidifier, and providing pain relief as needed.
Regularly monitoring vital signs, oxygen saturation, respiratory status, and symptoms progression. Documenting all findings and interventions accurately to ensure continuity of care.
Educating the patient and their family about the importance of adhering to the treatment plan, recognizing early signs of complications, and implementing measures to prevent recurrence.
Regular evaluation and monitoring are essential to assess the effectiveness of the nursing care plan and make necessary adjustments. Key components include:
Regularly assessing the patient's symptoms, including the frequency, intensity, and characteristics of cough, sputum production, and dyspnea.
Monitoring vital signs, including body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, to detect any changes in the patient's condition.
Evaluating oxygen saturation levels regularly to ensure adequate oxygenation and adjusting oxygen therapy as needed.
Evaluating the patient's response to medications and other interventions, and adjusting the care plan as needed to achieve optimal outcomes.
Seeking feedback from the patient and their family regarding the effectiveness of the care plan and their satisfaction with the care provided.
Implementing preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia and associated complications. Key strategies include:
Ensuring the patient receives recommended vaccinations, such as the flu and pneumococcal vaccines, to prevent respiratory infections.
Encouraging good hand hygiene practices to reduce the spread of infections, particularly during cold and flu season.
Encouraging smoking cessation and providing resources and support to help patients quit smoking, which is a major risk factor for respiratory conditions.
Minimizing exposure to environmental irritants, such as air pollution, allergens, and occupational hazards, that can trigger or exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
Promoting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate hydration, to support overall respiratory health.
Creating and implementing a nursing care plan for pneumonia involves a comprehensive approach that includes assessment, diagnosis, intervention, and evaluation. By addressing the underlying cause of the symptoms and providing appropriate interventions, nurses can help alleviate discomfort, prevent complications, and promote patient recovery. This guide serves as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals involved in the care of patients with pneumonia, providing the knowledge and tools needed to offer effective and compassionate care.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights on nutrition, meal planning, and healthy eating habits. Contact our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline at +91-8047190955 for assistance.
Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and is classified based on the causative agent and the location where the infection was acquired (community-acquired, hospital-acquired, or healthcare-associated). The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, infants, and those with chronic illnesses.
The first step in creating a nursing care plan for pneumonia is a comprehensive assessment. Key aspects of the assessment include:
Creating and implementing a nursing care plan for pneumonia involves a comprehensive approach that includes assessment, diagnosis, intervention, and evaluation. By addressing the underlying cause of the symptoms and providing appropriate interventions, nurses can help alleviate discomfort, prevent complications, and promote patient recovery. This guide serves as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals involved in the care of patients with pneumonia, providing the knowledge and tools needed to offer effective and compassionate care.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





