Developing an effective nursing care plan for patients with burns involves thorough assessment, diagnosis, and intervention. This guide provides essential information on creating and implementing nursing diagnoses for burns.
Blog
Comprehensive Guide to Nursing Diagnosis for Burns
Developing an effective nursing care plan for patients with burns involves thorough assessment, diagnosis, and intervention. Burns can cause significant physical and emotional trauma, and proper care is essential to ensure recovery and prevent complications. This comprehensive guide provides essential information on creating and implementing nursing diagnoses for burns, ensuring patient recovery and comfort.
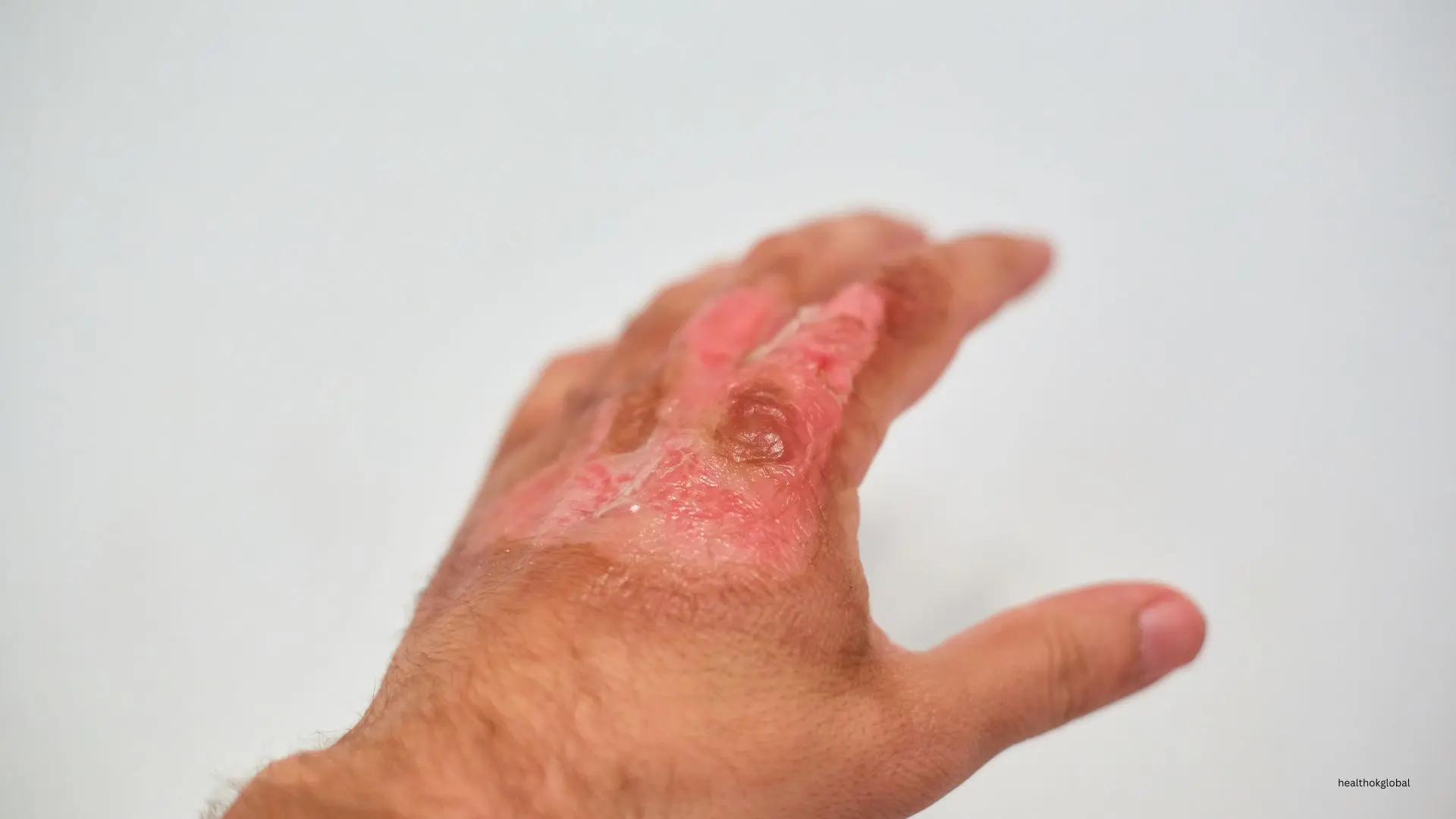
Burns are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. They are classified based on depth and extent: first-degree burns (superficial), second-degree burns (partial-thickness), and third-degree burns (full-thickness). The severity of burns can range from minor to life-threatening, requiring specialized care and treatment.
The first step in creating a nursing care plan for burns is a comprehensive assessment. Key aspects of the assessment include:
Gathering a detailed patient history, including the cause of the burn, the time of injury, and any pre-existing medical conditions.
Conducting a thorough physical examination to assess the extent, depth, and location of the burns, as well as the patient's vital signs and overall condition.
Using tools such as the Rule of Nines or the Lund and Browder chart to estimate the total body surface area (TBSA) affected by burns.
Evaluating the patient's pain level and providing appropriate pain management interventions.
Based on the assessment, the following nursing diagnoses may be identified for a patient with burns:
Related to thermal injury, as evidenced by the presence of burns, blisters, and skin breakdown.
Related to tissue damage and inflammation, as evidenced by the patient's report of pain and discomfort.
Related to open wounds and compromised skin barrier, as evidenced by the presence of burns and potential exposure to pathogens.
Related to fluid loss through burn wounds and evaporation, as evidenced by signs of dehydration and changes in vital signs.
Related to pain, swelling, and the location of burns, as evidenced by the patient's limited ability to move or perform activities of daily living.
Nursing interventions for managing burns focus on relieving symptoms, addressing the underlying cause, and preventing complications. Key interventions include:
Cleansing and dressing burn wounds using sterile techniques to prevent infection and promote healing. Applying topical antibiotics and changing dressings as prescribed.
Administering prescribed pain medications, using non-pharmacological pain relief methods, and regularly assessing pain levels to ensure adequate pain control.
Administering intravenous fluids to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance, especially in patients with extensive burns.
Implementing strict infection control measures, such as hand hygiene, aseptic techniques, and isolation precautions if necessary.
Providing a high-protein, high-calorie diet to support healing and recovery. Using enteral or parenteral nutrition if the patient is unable to eat orally.
Encouraging gentle exercises and physical therapy to maintain joint mobility and prevent contractures. Assisting with activities of daily living as needed.
Providing emotional support and counseling to help the patient cope with the trauma of the burn injury. Involving mental health professionals if necessary.
Regularly monitoring vital signs, fluid balance, wound healing, and signs of complications. Documenting all findings and interventions accurately to ensure continuity of care.
Educating the patient and their family about wound care, pain management, signs of infection, and measures to promote healing and prevent further injury.
Regular evaluation and monitoring are essential to assess the effectiveness of the nursing care plan and make necessary adjustments. Key components include:
Regularly assessing the condition of burn wounds, including the presence of infection, changes in size or depth, and signs of healing.
Monitoring the patient's pain levels and adjusting pain management strategies as needed to ensure adequate relief.
Evaluating fluid balance by monitoring fluid intake and output, and assessing signs of dehydration or fluid overload.
Watching for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, discharge, fever, or changes in vital signs.
Assessing the patient's physical mobility and range of motion, and implementing measures to maintain or improve mobility.
Regularly evaluating the patient's emotional and psychological well-being, and providing support and counseling as needed.
Seeking feedback from the patient and their family regarding the effectiveness of the care plan and their satisfaction with the care provided.
Implementing preventive measures can help reduce the risk of burns and associated complications. Key strategies include:
Educating patients and families about fire safety measures, such as installing smoke detectors, having fire extinguishers, and creating a fire escape plan.
Promoting safe handling and storage of chemicals to prevent chemical burns, including using protective equipment and following safety guidelines.
Teaching electrical safety practices to prevent electrical burns, such as avoiding overloaded outlets and using grounded appliances.
Encouraging the use of sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure to prevent sunburns.
Educating patients and families about basic first aid measures for burns, such as cooling the burn with water and seeking medical attention for severe burns.
Creating and implementing a nursing care plan for burns involves a comprehensive approach that includes assessment, diagnosis, intervention, and evaluation. By addressing the underlying cause of the injury and providing appropriate interventions, nurses can help alleviate discomfort, prevent complications, and promote patient recovery. This guide serves as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals involved in the care of patients with burns, providing the knowledge and tools needed to offer effective and compassionate care.
Burns are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. They are classified based on depth and extent: first-degree burns (superficial), second-degree burns (partial-thickness), and third-degree burns (full-thickness). The severity of burns can range from minor to life-threatening, requiring specialized care and treatment.
The first step in creating a nursing care plan for burns is a comprehensive assessment. Key aspects of the assessment include:
Nursing interventions for managing burns focus on relieving symptoms, addressing the underlying cause, and preventing complications. Key interventions include:
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.