A nursing diagnosis for pneumonia involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition and the development of a tailored care plan.
Blog
Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia: Key Considerations
A nursing diagnosis for pneumonia involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition and the development of a tailored care plan. Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that can lead to severe complications if not managed effectively. This guide covers key considerations for nursing diagnosis and management of pneumonia, including the identification of symptoms, risk factors, and appropriate interventions.
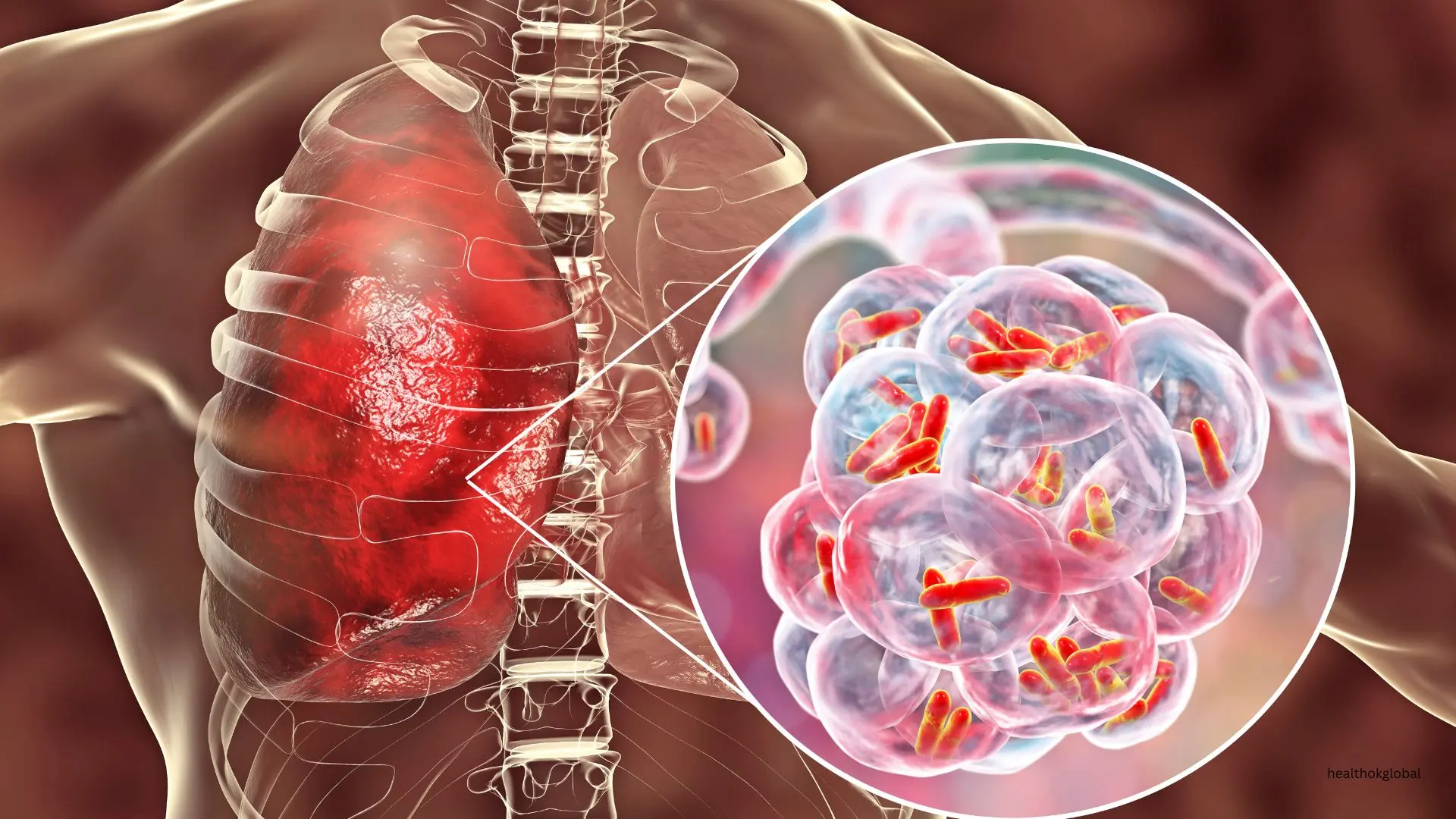
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli). The alveoli may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It can affect individuals of all ages but is particularly dangerous for young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
A persistent cough that may produce mucus or phlegm.
High fever accompanied by chills and sweating.
Difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breathing.
Sharp or stabbing pain in the chest that worsens with deep breathing or coughing.
General feeling of tiredness or weakness.
Confusion or changes in mental awareness, especially in older adults.
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing pneumonia, including:
Infants and young children, as well as adults over the age of 65, are at higher risk.
Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and diabetes can increase the risk.
Individuals with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, or organ transplants are more susceptible to pneumonia.
Smoking damages the lungs and impairs the body's ability to fight infections.
Being hospitalized, especially in an intensive care unit (ICU), increases the risk of hospital-acquired pneumonia.
A thorough nursing assessment is essential for diagnosing and managing pneumonia. Key components of the assessment include:
Gathering information about the patient's medical history, symptoms, and risk factors.
Conducting a physical examination to assess respiratory rate, breath sounds, and the presence of any signs of respiratory distress.
Ordering and interpreting diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures.
Based on the assessment findings, several nursing diagnoses may be relevant for patients with pneumonia, including:
Related to increased mucus production and inflammation in the airways.
Related to fluid-filled alveoli and impaired oxygenation.
Related to fatigue and shortness of breath.
Related to chest pain and discomfort.
Related to weakened immune response and potential for secondary infections.
Effective nursing interventions are crucial for managing pneumonia and promoting recovery. Key interventions include:
Implementing measures to maintain a clear airway, such as positioning, suctioning, and encouraging deep breathing and coughing.
Administering supplemental oxygen to improve oxygenation and relieve hypoxia.
Administering prescribed medications, including antibiotics, antipyretics, and bronchodilators.
Ensuring adequate hydration and nutrition to support the immune system and overall health.
Educating the patient and family about pneumonia, its treatment, and preventive measures.
A comprehensive nursing diagnosis for pneumonia involves a thorough assessment of the patient's condition and the development of a tailored care plan. By identifying the key symptoms, risk factors, and appropriate interventions, healthcare professionals can effectively manage pneumonia and promote patient recovery. Continued education and research are essential for improving the diagnosis and management of pneumonia, ultimately reducing its impact on patients and healthcare systems.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights on nutrition, meal planning, and healthy eating habits. Contact our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline at +91-8047190955 for assistance.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli). The alveoli may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It can affect individuals of all ages but is particularly dangerous for young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





