Sore eyes, also known as eye irritation or eye discomfort, can be a common and bothersome problem affecting people of all ages.
Blog
Understanding Sore Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Sore eyes, also known as eye irritation or eye discomfort, can be a common and bothersome problem affecting people of all ages. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sore eyes is essential for maintaining good eye health and alleviating discomfort.
Exposure to environmental irritants such as smoke, dust, pollen, and pollutants can lead to sore eyes. Additionally, prolonged screen time, especially with digital devices, can contribute to eye strain and discomfort.
Allergies to pollen, pet dander, mold, or other allergens can cause redness, itching, and swelling of the eyes, leading to soreness and discomfort.
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when tears evaporate too quickly. This can result in symptoms such as dryness, burning, and irritation of the eyes.
Bacterial or viral infections such as conjunctivitis (pink eye) can cause soreness, redness, and discharge from the eyes. These infections may require medical treatment to resolve.
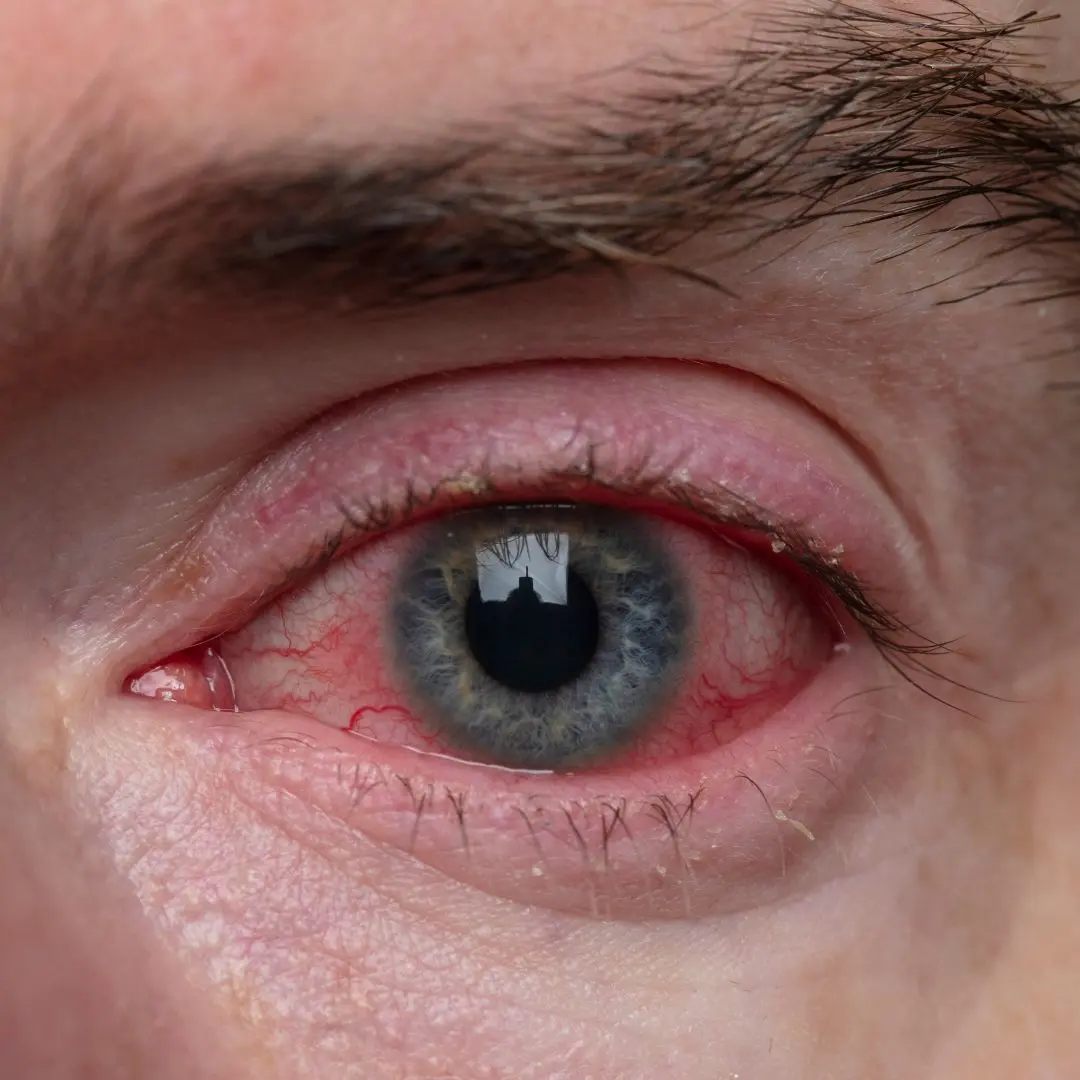
One of the most common symptoms of sore eyes is redness or bloodshot eyes, which may be accompanied by inflammation of the blood vessels in the eyes.
Sore eyes often feel itchy or irritated, prompting the urge to rub or scratch the eyes, which can exacerbate the discomfort.
A burning sensation or feeling of grittiness in the eyes is another hallmark symptom of sore eyes, particularly in cases of dry eye syndrome or environmental irritants.
People with sore eyes may experience increased sensitivity to light (photophobia), making it uncomfortable to be in brightly lit environments.
Artificial tears or lubricating eye drops can help relieve dryness and provide temporary relief from soreness and irritation.
Applying warm compresses to the eyes can help improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and soothe soreness.
Avoiding exposure to environmental irritants such as smoke, dust, and allergens can help prevent sore eyes.
In cases of severe or persistent sore eyes, prescription medications such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or antibiotic eye drops may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and treat underlying conditions.
If you spend long hours in front of a screen, take regular breaks to rest your eyes and reduce the risk of eye strain and discomfort.
Maintaining good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding touching your eyes, can help prevent the spread of infections that can cause sore eyes.
When engaging in activities that may expose your eyes to potential hazards, such as yard work or sports, wear protective eyewear to prevent injuries and irritation.
While mild cases of sore eyes may resolve on their own or with home remedies, it's important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, such as severe pain, vision changes, or discharge from the eyes. These could be signs of a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt treatment.
Sore eyes can be a frustrating and uncomfortable problem, but with proper understanding and care, they can often be effectively managed and relieved. By identifying potential causes, practicing preventive measures, and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, you can maintain good eye health and minimize discomfort associated with sore eyes. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, don't hesitate to consult with an eye care professional for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights on nutrition, meal planning, and healthy eating habits. Contact our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline at +91-8047190955 for assistance.
While mild cases of sore eyes may resolve on their own or with home remedies, it's important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, such as severe pain, vision changes, or discharge from the eyes. These could be signs of a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt treatment.
Exposure to environmental irritants such as smoke, dust, pollen, and pollutants can lead to sore eyes. Additionally, prolonged screen time, especially with digital devices, can contribute to eye strain and discomfort.
This section covers Symptoms of Sore Eyes in detail.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.