Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) is an enzyme crucial for the production of thyroid hormones.
Blog
Understanding TPO: Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and Their Health Implications
Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) is an enzyme crucial for the production of thyroid hormones. It is found in the thyroid gland and plays a significant role in the synthesis of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). TPO is involved in the iodination of tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin, which is a critical step in the production of these hormones. Proper functioning of TPO is essential for maintaining normal thyroid hormone levels, which are vital for regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
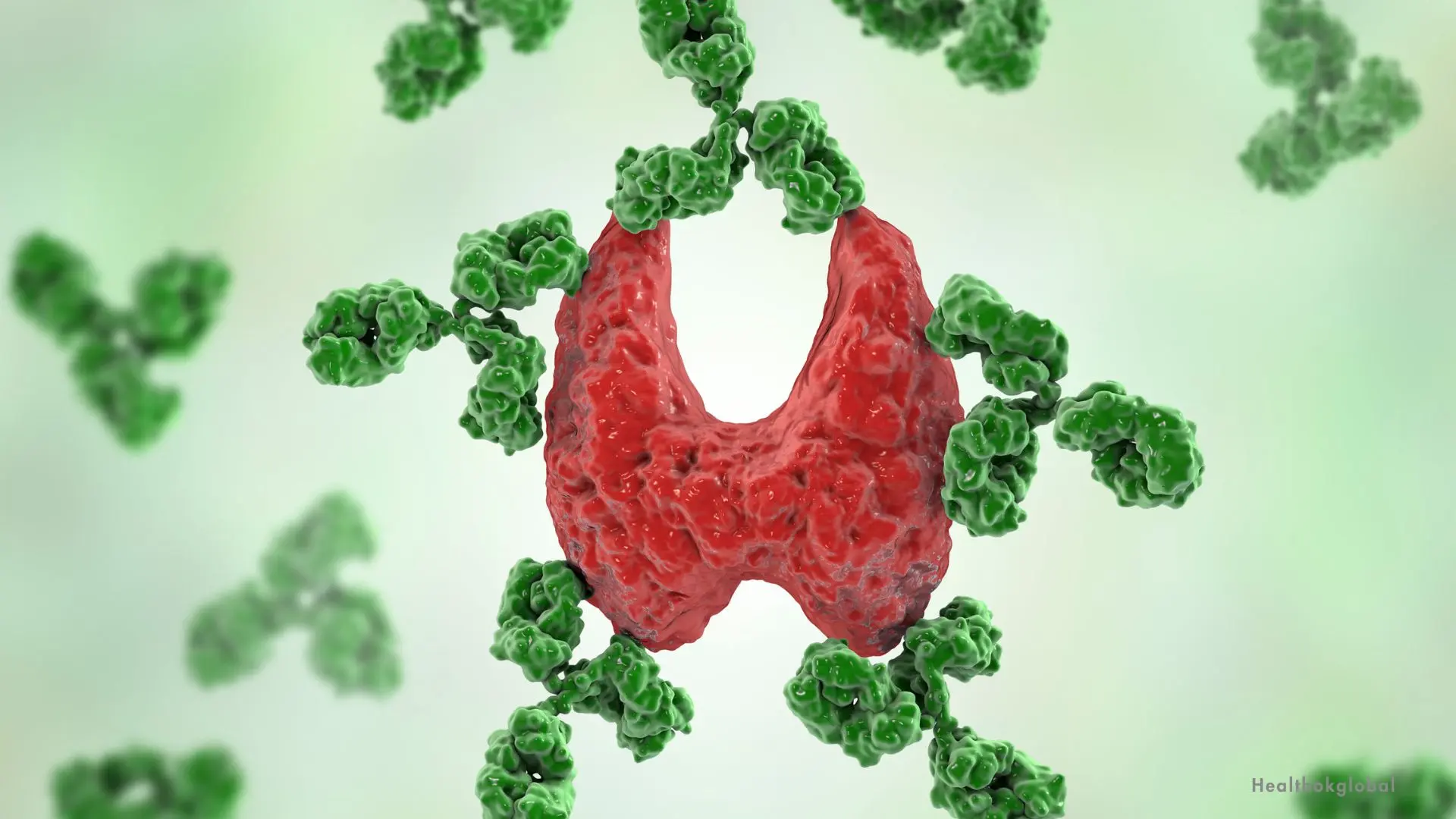
TPO antibodies are autoantibodies directed against the thyroid peroxidase enzyme. The presence of these antibodies indicates an autoimmune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own thyroid gland. This immune response can lead to thyroid dysfunction and is commonly associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease.
This is the most common cause of hypothyroidism, where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and impaired thyroid hormone production. High levels of TPO antibodies are typically present in individuals with Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
An autoimmune disorder that causes hyperthyroidism, characterized by overactive thyroid hormone production. While TPO antibodies can be present, other autoantibodies, such as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI), are more directly involved in Graves' disease.
Testing for TPO antibodies is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying autoimmune thyroid disorders. It helps healthcare providers diagnose the underlying cause of thyroid dysfunction and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Detecting TPO antibodies early can lead to timely intervention, preventing the progression of thyroid disorders and associated complications.
Regular TPO testing can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment for autoimmune thyroid conditions and adjust therapeutic strategies as needed.
Individuals with a family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases can benefit from TPO testing to assess their risk and take preventive measures.
The TPO test is a simple blood test that measures the level of thyroid peroxidase antibodies in the bloodstream. The procedure is straightforward and involves the following steps:
Generally, no special preparation is needed for the TPO test. Patients may be advised to inform their healthcare provider about any medications or supplements they are taking, as some can affect test results.
A healthcare professional draws a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm.
The blood sample is sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed for the presence and concentration of TPO antibodies.
Results are typically available within a few days. High levels of TPO antibodies indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorder.
Interpreting TPO test results involves understanding what the levels of TPO antibodies indicate about thyroid health. Normal and elevated levels can provide insights into potential thyroid dysfunction.
TPO antibody levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory, but generally, a normal range is less than 35 IU/mL.
Elevated TPO antibody levels suggest the presence of an autoimmune thyroid disorder. Higher levels are typically associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease.
Elevated TPO antibody levels should be interpreted in conjunction with other thyroid function tests, such as TSH, T3, and T4, for a comprehensive assessment of thyroid health.
High levels of TPO antibodies have significant implications for thyroid health and overall well-being. They indicate an ongoing autoimmune attack on the thyroid gland, which can lead to various thyroid dysfunctions.
In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the autoimmune attack damages the thyroid gland, leading to reduced thyroid hormone production and hypothyroidism. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and cold intolerance.
In Graves' disease, the autoimmune response can lead to excessive thyroid hormone production, causing hyperthyroidism. Symptoms include weight loss, increased appetite, anxiety, and heat intolerance.
Chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland due to high TPO antibody levels can cause thyroid enlargement (goiter) and discomfort.
Managing autoimmune thyroid disorders involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to maintain thyroid health and prevent complications.
Depending on the type and severity of thyroid dysfunction, medications such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism or antithyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism may be prescribed.
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can support thyroid health and overall well-being.
Regular follow-up appointments and thyroid function tests are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
While autoimmune thyroid disorders cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and interventions may help reduce TPO antibody levels and support thyroid health.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly selenium and iodine, can support thyroid function. Avoiding processed foods and reducing gluten intake may also benefit individuals with autoimmune thyroid conditions.
Chronic stress can exacerbate autoimmune responses. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress levels.
Early detection and management of thyroid dysfunction can prevent complications. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring thyroid health.
Understanding TPO and its role in thyroid health is crucial for diagnosing and managing autoimmune thyroid disorders. TPO antibodies serve as important markers for identifying conditions such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. Regular testing, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle modifications can help manage these conditions effectively and improve overall well-being. By staying informed about TPO antibodies and their implications, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining thyroid health and seeking timely medical intervention when necessary. Regular consultations with healthcare providers and adherence to recommended health practices are essential for managing autoimmune thyroid disorders and ensuring optimal health.
The TPO test is a simple blood test that measures the level of thyroid peroxidase antibodies in the bloodstream. The procedure is straightforward and involves the following steps:
TPO antibodies are autoantibodies directed against the thyroid peroxidase enzyme. The presence of these antibodies indicates an autoimmune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own thyroid gland. This immune response can lead to thyroid dysfunction and is commonly associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease.
Interpreting TPO test results involves understanding what the levels of TPO antibodies indicate about thyroid health. Normal and elevated levels can provide insights into potential thyroid dysfunction.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.