Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in overall health, especially for individuals managing conditions like diabetes.
Blog
Understanding and Managing Blood Sugar Fasting PP
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in overall health, especially for individuals managing conditions like diabetes. Understanding the significance of fasting and postprandial (PP) blood sugar levels is essential for effective management and prevention of complications. Let's delve into what blood sugar fasting PP entails and how to manage it effectively.
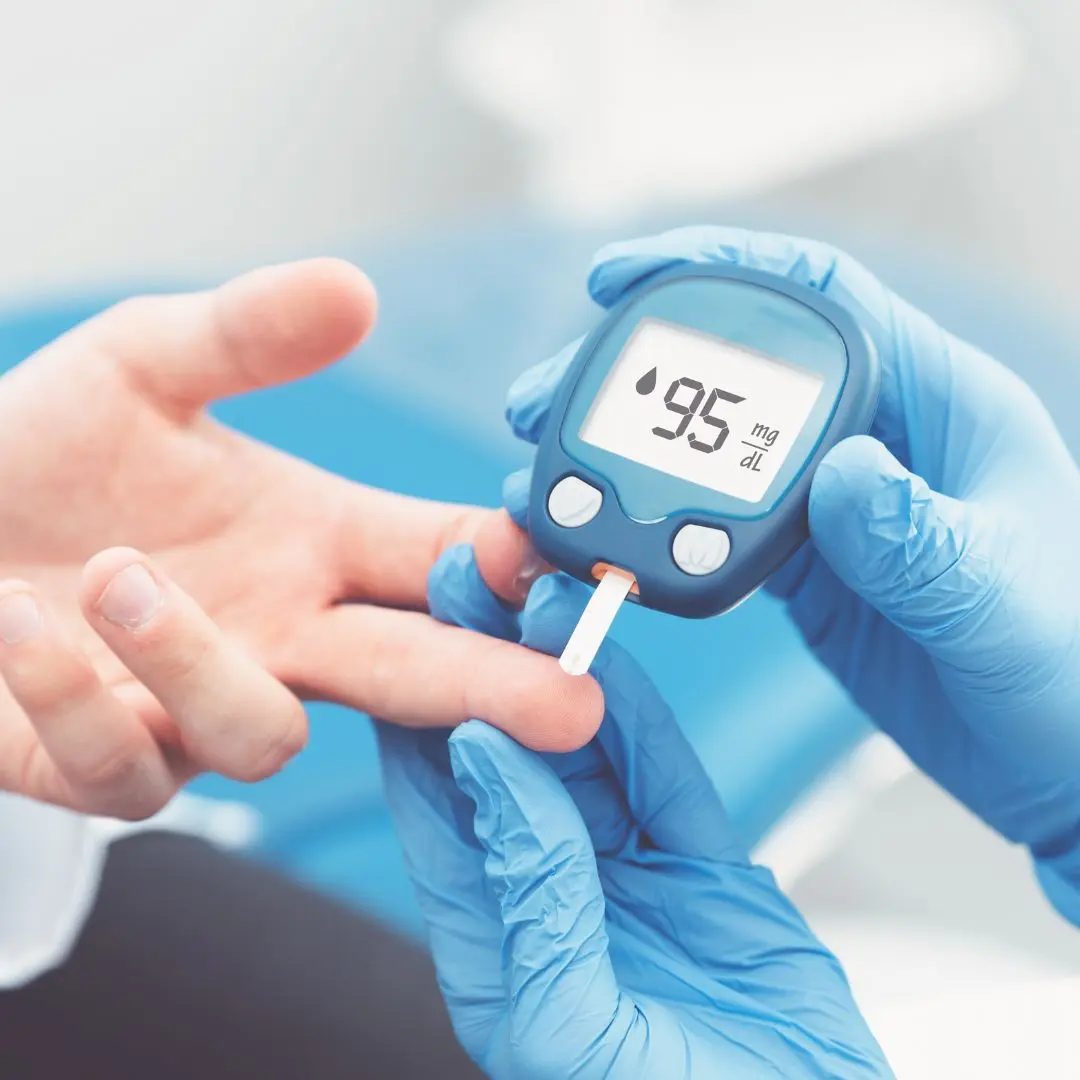
Blood sugar fasting refers to the glucose level in the blood after an overnight fast, typically before breakfast. It provides a baseline measurement of how the body processes glucose in the absence of food intake. On the other hand, postprandial (PP) blood sugar levels are measured after consuming a meal, usually two hours afterward. PP levels indicate how the body responds to food and regulates glucose after digestion.
Monitoring blood sugar levels, both fasting and PP, is vital for individuals with diabetes to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) episodes. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to diabetic complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Conversely, low blood sugar levels can cause dizziness, weakness, and even loss of consciousness if left untreated.
Several factors can influence blood sugar fasting PP levels, including diet, physical activity, medication, stress, and underlying health conditions. Carbohydrate-rich foods, sugary beverages, and large meals can cause postprandial spikes in blood sugar levels. Similarly, inadequate insulin production or insulin resistance can lead to elevated fasting blood sugar levels.
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Here are some strategies to help manage blood sugar fasting PP effectively:
Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Monitor carbohydrate intake and choose low-glycemic index foods to minimize blood sugar spikes.
Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels.
Take prescribed medications, such as oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin injections, as directed by healthcare professionals to control blood sugar levels.
Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to lower cortisol levels and prevent stress-induced blood sugar fluctuations.
Regularly monitor blood sugar levels using a glucometer to track fasting and postprandial readings. Keep a record of results to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
In conclusion, understanding and managing blood sugar fasting PP levels are essential for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications and maintain overall health. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, adhering to medication regimens, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, individuals can achieve optimal blood sugar control and minimize the risk of diabetic complications. Consultation with healthcare professionals is crucial for personalized management plans and guidance tailored to individual needs.
Blood sugar fasting refers to the glucose level in the blood after an overnight fast, typically before breakfast. It provides a baseline measurement of how the body processes glucose in the absence of food intake. On the other hand, postprandial (PP) blood sugar levels are measured after consuming a meal, usually two hours afterward. PP levels indicate how the body responds to food and regulates glucose after digestion.
Monitoring blood sugar levels, both fasting and PP, is vital for individuals with diabetes to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) episodes. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to diabetic complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Conversely, low blood sugar levels can cause dizziness, weakness, and even loss of consciousness if left untreated.
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Here are some strategies to help manage blood sugar fasting PP effectively:
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.