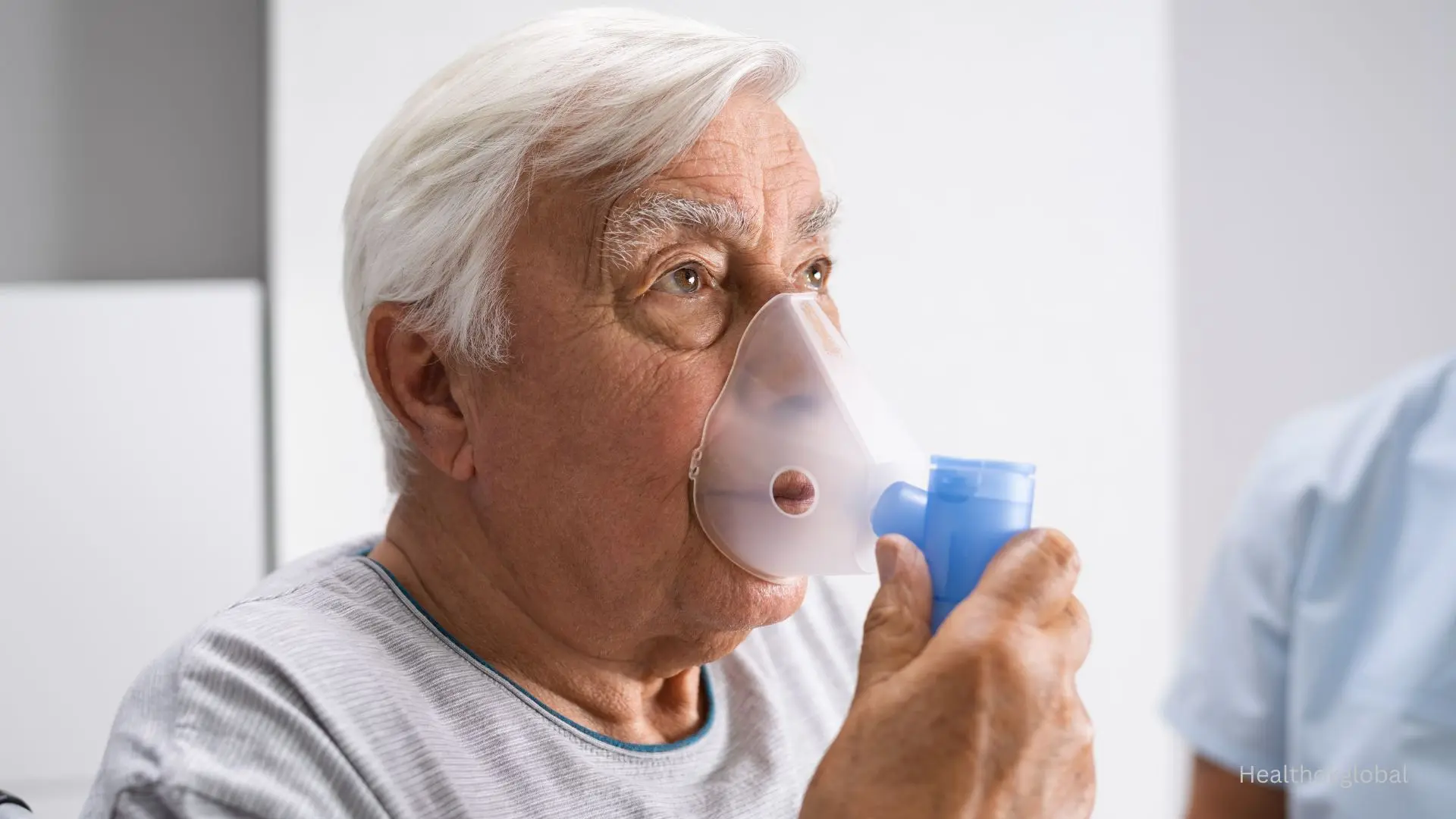
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious infectious disease that demands careful dietary management to aid recovery and treatment effectiveness.

Blog
Tuberculosis Recovery: 6 Harmful Foods You Must Avoid
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to be one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, affecting over 10 million people annually according to WHO. While medication remains the cornerstone of treatment, diet plays a crucial role in boosting immunity, enhancing medication effectiveness, and ensuring a quicker recovery. This blog explores specific foods TB patients should avoid to prevent complications and support healing.
Malnutrition and tuberculosis often go hand in hand. TB increases the body's metabolic rate and weakens the immune system, making nutritional support essential. A poor diet can worsen fatigue, weight loss, and side effects from medication. Thus, avoiding harmful foods is just as important as consuming the right ones.
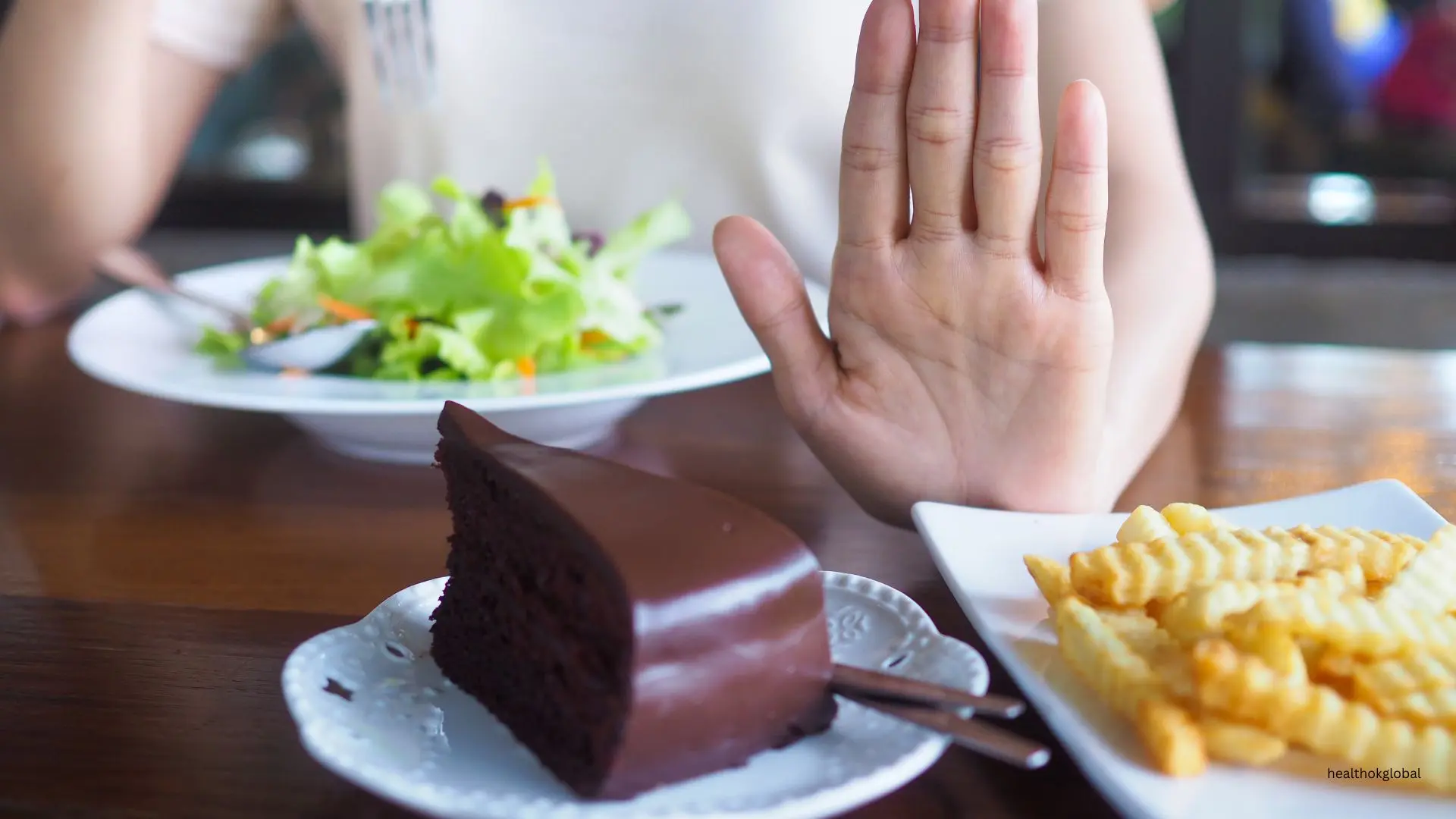
These foods can impair immunity, hinder drug absorption, or aggravate TB symptoms:
Alcohol interferes with TB medications, especially Rifampicin and Isoniazid, increasing the risk of liver toxicity. It also weakens immune defenses, making the body more susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Caffeine can irritate the stomach lining, especially during antibiotic treatment, and may worsen restlessness or insomnia. It's also known to affect the absorption of TB drugs.
Foods high in trans fats, sugar, and preservatives (like chips, pastries, and instant noodles) offer little nutritional value. They contribute to inflammation, suppress immunity, and lead to unnecessary weight gain.
High intake of saturated fats from red meats can increase inflammation and may aggravate side effects like nausea or indigestion during TB therapy.
While calcium is beneficial, full-fat dairy products can be hard to digest and contribute to cholesterol imbalance. Opt for skimmed milk or low-fat curd instead.
Chilies and fried foods can worsen gastritis—a common side effect of TB medication. Stick to lightly spiced and boiled foods for better gut health.
A balanced, immune-boosting diet supports recovery. Focus on:
Proteins help rebuild muscle mass lost due to weight loss. Include dal, lentils, tofu, paneer, lean chicken, fish, and eggs.
Colorful produce provides antioxidants and vitamins like A, C, and E, essential for immune strength. Citrus fruits, carrots, and spinach are excellent choices.
Oats, brown rice, and whole wheat chapatis provide sustained energy and improve gut health.
Hydration is key. Drink 8–10 glasses of water daily. Herbal teas like ginger or tulsi can help manage nausea and improve immunity.
Common side effects of TB treatment include digestive discomfort and loss of appetite. Here are tips to address them nutritionally:
Ginger tea, dry toast, and smaller meals throughout the day can help manage nausea.
Nutrient-dense smoothies and homemade soups can deliver calories without making you feel too full.
Use the BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) temporarily. Avoid high-fiber or dairy items during this phase.
Recovery from TB may take several months. Ongoing dietary monitoring can prevent relapse and enhance recovery. Here’s how:
Monitoring weight ensures that calorie intake is adequate and muscle loss is avoided.
Vitamin D, B-complex, and zinc may be recommended by your doctor. Avoid self-prescribing.
A dedicated home caretaker can help prepare meals, track symptoms, and manage follow-ups.
Yes, but prefer low-fat milk to avoid digestion issues. Milk is a good source of protein and calcium.
Excessive caffeine can interfere with medication and worsen gastric discomfort. Limit to one small cup a day if tolerated.
No, TB is not spread via food. Learn more from our guide: Is Asthma a Communicable Disease?
Not ideally. Medication is crucial, but without a supportive diet, recovery may be slower and less effective.
Managing TB goes beyond taking medications—it’s about supporting your body through conscious nutrition. By avoiding harmful foods and following a nutrient-rich plan, patients can speed up recovery, minimize side effects, and regain strength. With the help of caretakers, regular medical guidance, and healthy choices, TB management becomes not just possible—but successful.
HealthOK Global helps you build a fruit-powered wellness routine. Contact our experts for guidance or chat with our FREE 24x7 helpline on WhatsApp.
Malnutrition and tuberculosis often go hand in hand. TB increases the body's metabolic rate and weakens the immune system, making nutritional support essential. A poor diet can worsen fatigue, weight loss, and side effects from medication. Thus, avoiding harmful foods is just as important as consuming the right ones.
A balanced, immune-boosting diet supports recovery. Focus on:
Yes, but prefer low-fat milk to avoid digestion issues. Milk is a good source of protein and calcium.
Excessive caffeine can interfere with medication and worsen gastric discomfort. Limit to one small cup a day if tolerated.
No, TB is not spread via food. Learn more from our guide: Is Asthma a Communicable Disease?
Not ideally. Medication is crucial, but without a supportive diet, recovery may be slower and less effective.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.