Bone tuberculosis, also known as skeletal tuberculosis, is a form of extrapulmonary TB that affects the bones and joints.
Blog
Bone Tuberculosis: Comprehensive Guide
Bone tuberculosis, also known as skeletal tuberculosis, is a form of extrapulmonary TB that affects the bones and joints. This condition is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the same bacterium responsible for pulmonary tuberculosis. Bone TB primarily affects the spine, but it can also involve other bones and joints. This comprehensive guide explores the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bone tuberculosis, highlighting the importance of early detection and management.
The symptoms of bone tuberculosis can vary depending on the affected area but generally include the following:
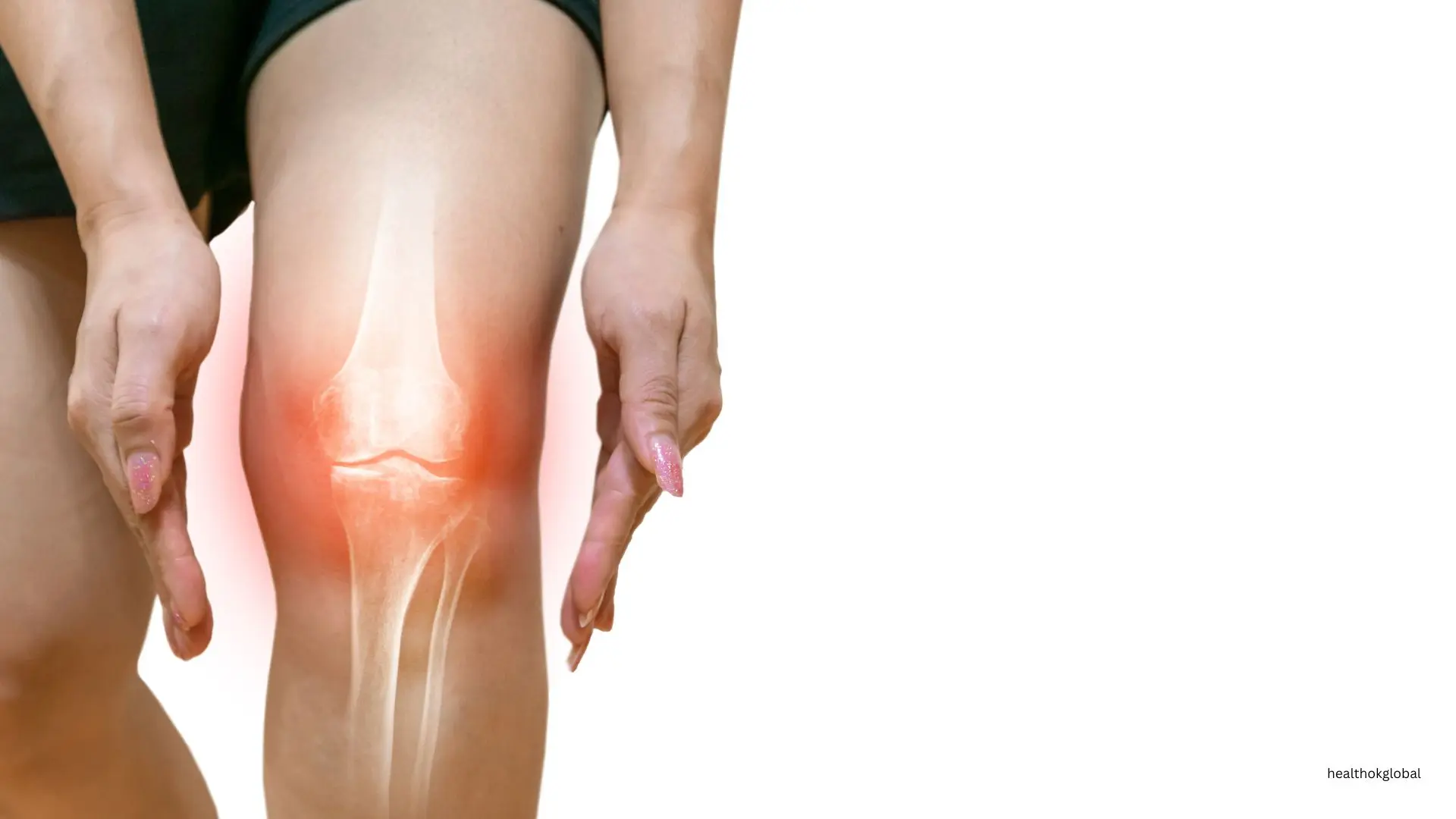
Persistent pain in the affected bone or joint is a common symptom. The pain may be severe and worsen with movement.
Swelling and tenderness in the affected area can occur, often accompanied by warmth and redness.
Limited range of motion and stiffness in the affected joint can lead to difficulty in performing daily activities.
Systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss may also be present.
In some cases, an abscess or sinus tract may develop, draining pus from the infected site.
Diagnosing bone tuberculosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Key diagnostic methods include:
A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial for identifying symptoms and risk factors associated with bone TB.
X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans are used to detect characteristic changes in the bones and joints, such as bone destruction and soft tissue involvement.
Blood tests, including the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), can indicate inflammation. Tuberculin skin tests and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) help identify TB infection.
A biopsy of the affected tissue followed by microbiological culture and histopathological examination confirms the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The treatment of bone tuberculosis involves a combination of medical and surgical approaches. Key treatment options include:
The cornerstone of TB treatment is a prolonged course of antitubercular drugs, including isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. The duration of treatment is typically 6-12 months.
Surgical intervention may be necessary in cases of severe bone destruction, abscess formation, or spinal instability. Procedures include debridement, abscess drainage, and spinal fusion.
Rehabilitation through physical therapy is essential for restoring mobility, strength, and function to the affected joints and muscles.
Pain relief is achieved through medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and other pain management techniques.
If left untreated, bone tuberculosis can lead to serious complications, including:
Severe cases of spinal TB can cause kyphosis (hunchback) and other deformities, leading to chronic pain and disability.
Compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots can result in neurological deficits, including paralysis and loss of sensation.
TB can cause extensive damage to the joints, leading to arthritis, joint instability, and functional impairment.
Persistent pain and disability can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with untreated or inadequately treated bone TB.
Preventing bone tuberculosis involves several public health measures and personal protective strategies:
The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine provides some protection against TB and is routinely administered in countries with high TB prevalence.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary TB can prevent the spread of the infection to bones and other organs.
Efforts to improve living conditions, reduce overcrowding, and ensure adequate nutrition are essential for controlling the spread of TB.
Bone tuberculosis is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. By addressing the broader issue of TB control and implementing preventive measures, we can reduce the incidence of bone tuberculosis and improve patient outcomes. Ongoing research and public health efforts are vital in the fight against TB and its complications.
HealthOK Global's dedicated care team provides essential healthcare assistance for the elderly in India, ensuring they receive comprehensive support in the comfort of their homes. From routine medical check-ups and medication management to personalized nursing care and emergency response services, our expert caregivers are committed to enhancing the quality of life for seniors. With our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline, you can reach us anytime at +91-8047190955 (India) or +1-888-462-1804 (USA) to ensure your loved ones receive the best possible care.
The symptoms of bone tuberculosis can vary depending on the affected area but generally include the following:
Diagnosing bone tuberculosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Key diagnostic methods include:
Bone tuberculosis is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. By addressing the broader issue of TB control and implementing preventive measures, we can reduce the incidence of bone tuberculosis and improve patient outcomes. Ongoing research and public health efforts are vital in the fight against TB and its complications.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





