Maintaining adequate blood oxygen levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Learn effective strategies to boost your blood oxygen levels naturally.
Blog
Increasing Blood Oxygen Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Maintaining adequate blood oxygen levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Blood oxygen levels indicate how well oxygen is being transported to the body's tissues, which is vital for cellular function and energy production. Low blood oxygen levels can lead to various health issues, including fatigue, shortness of breath, and decreased cognitive function. This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to naturally increase blood oxygen levels, improve respiratory health, and enhance overall vitality.
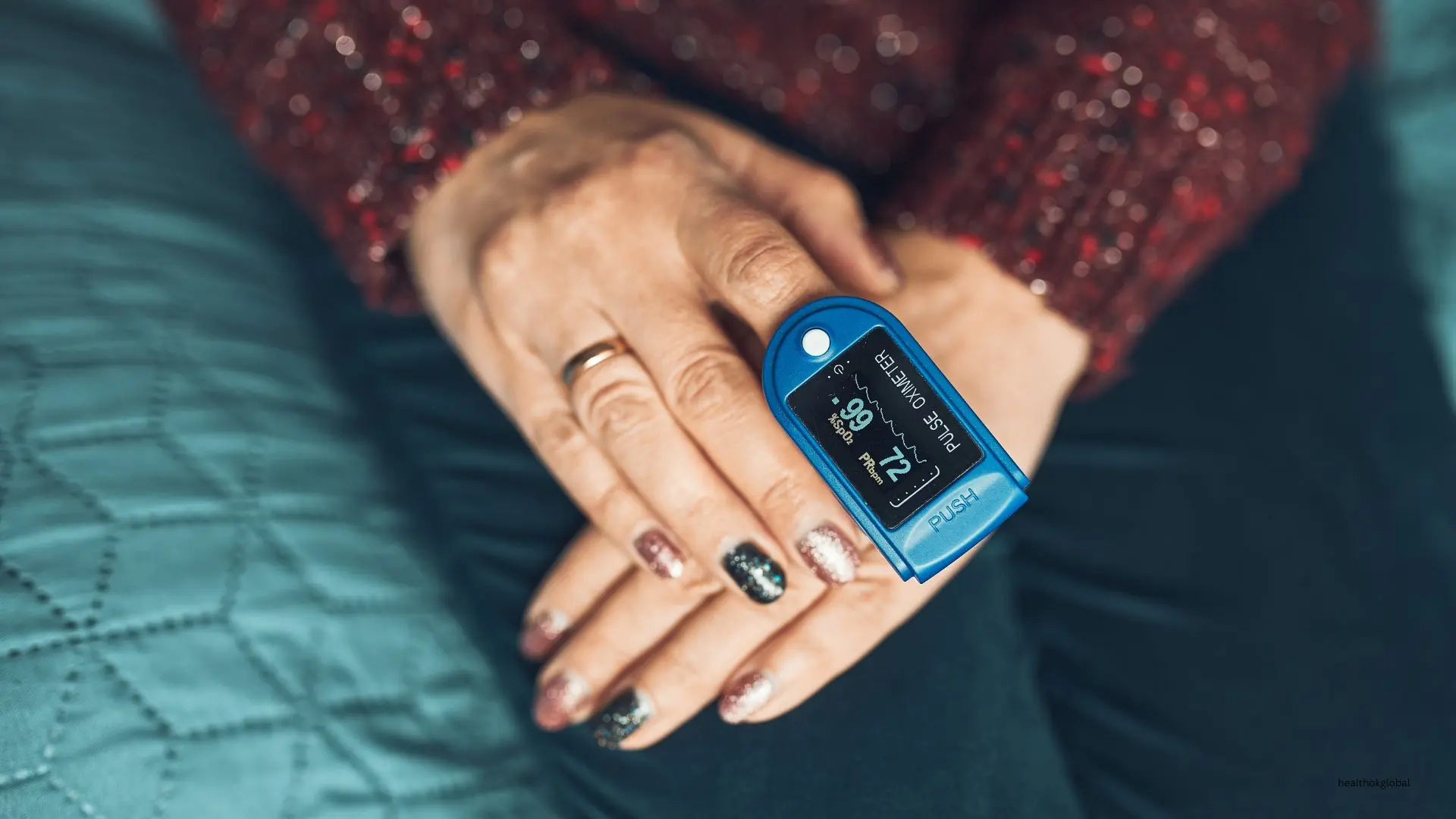
Blood oxygen levels, also known as oxygen saturation, are typically measured using a pulse oximeter. Normal oxygen saturation levels range between 95% and 100%. Levels below 90% are considered low and may indicate hypoxemia, a condition that requires medical attention. Several factors can influence blood oxygen levels, including lung function, heart health, and environmental conditions.
Various factors can contribute to low blood oxygen levels, including:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, and other lung conditions can impair oxygen exchange.
Heart conditions such as congestive heart failure and arrhythmias can affect oxygen delivery to the tissues.
Low levels of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying component of red blood cells, can lead to reduced oxygen saturation.
At high altitudes, the air contains less oxygen, which can result in lower blood oxygen levels.
Interrupted breathing during sleep can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood.
Lack of physical activity can reduce lung capacity and impair oxygen exchange.
The following strategies can help increase blood oxygen levels and improve overall respiratory health:
Also known as belly breathing, this exercise involves deep breathing using the diaphragm rather than the chest. To practice, sit or lie down comfortably, place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to rise, then exhale slowly through your mouth.
This technique helps keep airways open longer, allowing more oxygen to enter the lungs. Inhale slowly through your nose for two counts, then exhale through pursed lips for four counts.
Regular exercise enhances lung capacity, improves circulation, and increases the efficiency of oxygen exchange in the lungs. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week.
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall health and respiratory function. Include the following nutrients in your diet:
Foods such as lean meats, beans, spinach, and fortified cereals help maintain healthy hemoglobin levels, which are essential for oxygen transport.
Fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants, such as berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, protect lung tissue from oxidative damage.
Foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts reduce inflammation and improve lung function.
Drinking plenty of water keeps mucous membranes moist and facilitates oxygen transport.
Smoking damages lung tissue and reduces the efficiency of oxygen exchange. Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke. Additionally, limit exposure to environmental pollutants and allergens that can impair lung function.
Dry air can irritate the respiratory tract and reduce oxygen absorption. Using a humidifier adds moisture to the air, making it easier to breathe and improving oxygen levels, especially during dry weather or in air-conditioned environments.
Sleeping with your head elevated can help improve breathing and oxygen saturation, especially for individuals with sleep apnea or respiratory issues. Use an extra pillow or an adjustable bed to elevate your upper body.
Maintaining good posture ensures that your lungs have enough space to expand fully, promoting better oxygen exchange. Avoid slouching and practice sitting and standing with your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, supplemental oxygen therapy can help maintain adequate oxygen levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if oxygen therapy is appropriate for your needs.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of low blood oxygen levels, such as:
Difficulty breathing that does not improve with rest or home remedies.
Chest pain or pressure that may indicate a serious underlying condition.
Signs of confusion, disorientation, or changes in mental status.
Bluish discoloration of the lips, nails, or skin, indicating low oxygen levels.
Maintaining healthy blood oxygen levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By incorporating breathing exercises, physical activity, a balanced diet, and other lifestyle changes, you can naturally boost your oxygen levels and improve respiratory health. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options, especially if you have underlying health conditions. With these effective strategies, you can enhance your oxygen saturation and enjoy better health and vitality.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of low blood oxygen levels, such as:
Blood oxygen levels, also known as oxygen saturation, are typically measured using a pulse oximeter. Normal oxygen saturation levels range between 95% and 100%. Levels below 90% are considered low and may indicate hypoxemia, a condition that requires medical attention. Several factors can influence blood oxygen levels, including lung function, heart health, and environmental conditions.
For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, supplemental oxygen therapy can help maintain adequate oxygen levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if oxygen therapy is appropriate for your needs.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.