Explore the complexities of obesity, including its classification, diagnosis codes, and impact on health. Learn about Class 1, 2, and 3 obesity and effective solutions.
Obesity has become one of the most pressing public health challenges globally. More than just a cosmetic concern, obesity is a complex, chronic disease that significantly increases the risk of numerous health conditions. Understanding obesity—its causes, classification, and diagnosis—is critical to implementing the right strategies for treatment and prevention. This comprehensive guide breaks down the types of obesity, ICD-10 classifications, and real-world solutions, including lifestyle modifications and healthcare interventions.
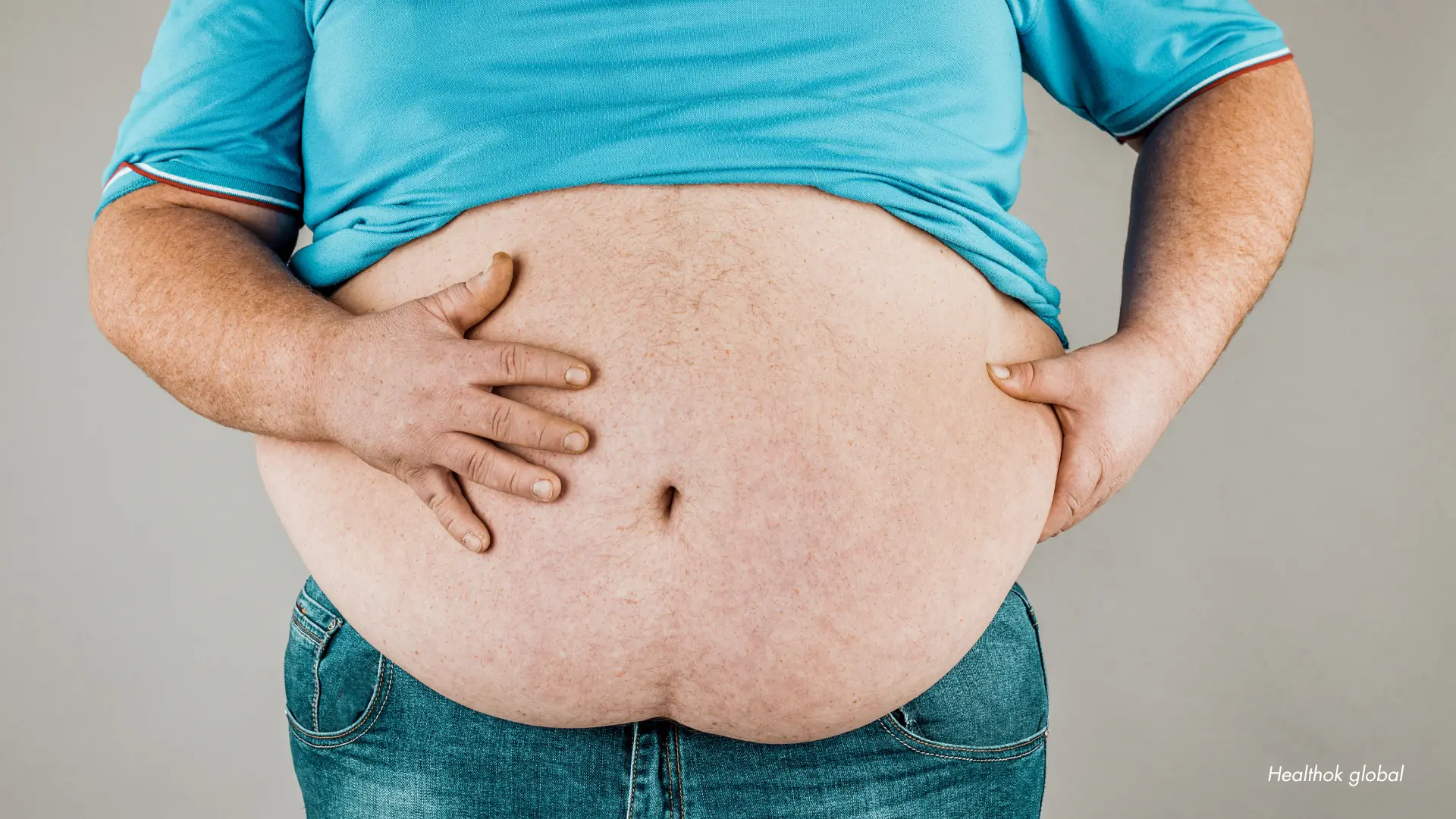
What Is Obesity?
Obesity is defined as an abnormal or excessive accumulation of body fat that presents a risk to health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher is categorized as obese. Obesity can reduce life expectancy and quality of life by contributing to diseases like type 2 diabetes, heart conditions, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Obesity ICD-10 and Diagnosis Code
In clinical settings, obesity is diagnosed using specific coding systems. The
ICD-10 code for obesity is
E66, with subcodes that differentiate among types:
- E66.0: Obesity due to excess calories
- E66.1: Drug-induced obesity
- E66.2: Morbid (severe) obesity with alveolar hypoventilation
- E66.9: Obesity, unspecified
These codes are vital for accurate documentation, insurance claims, and public health data collection.
Obesity Classification: Class 1 to Class 3
Obesity is categorized into three classes based on severity, primarily using BMI:
- Obesity Class 1 (BMI 30–34.9): Also known as low-risk obesity
- Obesity Class 2 (BMI 35–39.9): Moderate-risk obesity
- Obesity Class 3 (BMI ≥40): Also known as severe, extreme, or morbid obesity
These classes help clinicians determine the appropriate level of intervention and predict associated health risks. For instance,
Class 3 obesity is often associated with severe mobility issues and metabolic complications.
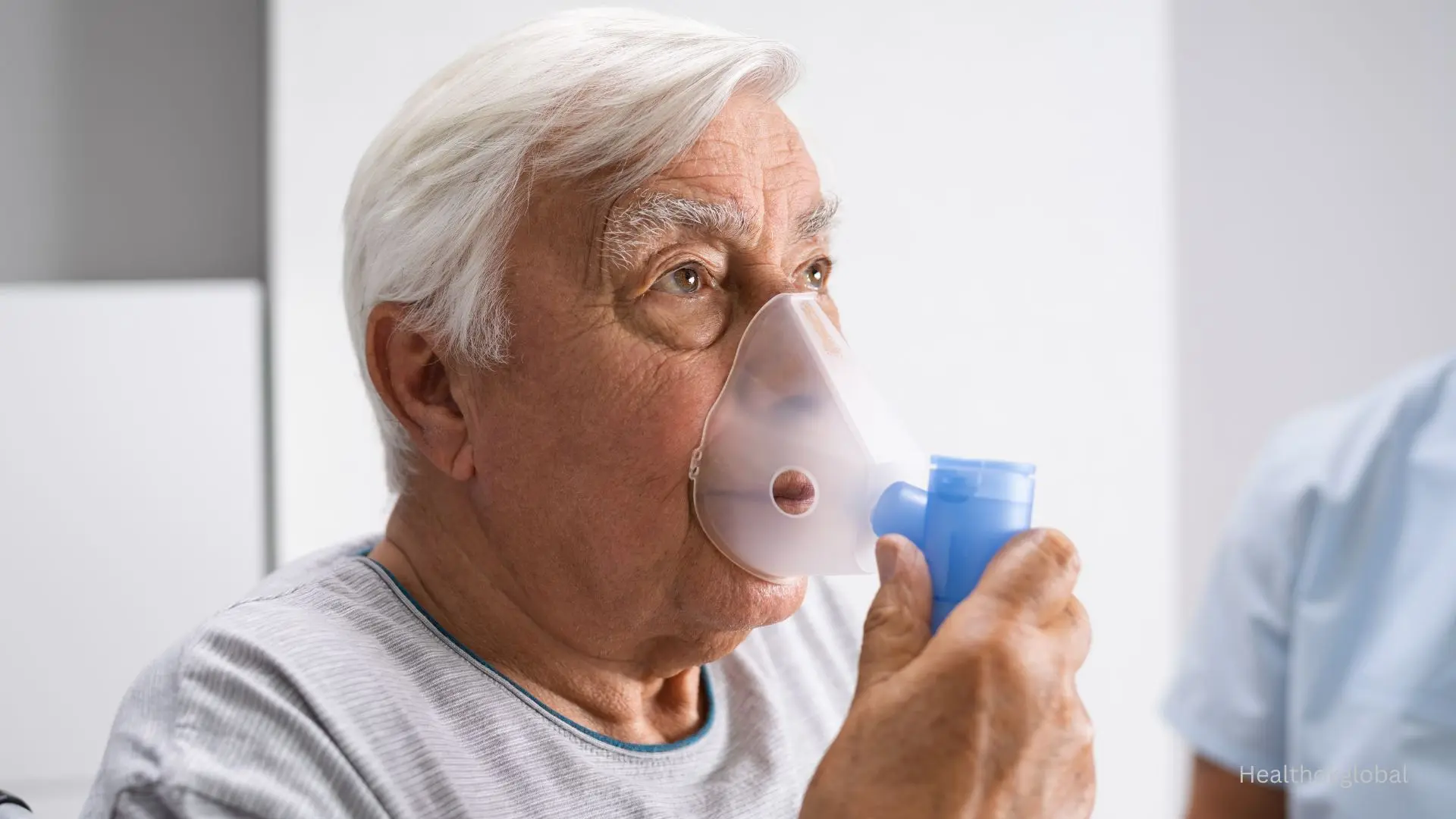
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS), also known as Pickwickian syndrome, is a serious condition where severely obese individuals have poor ventilation and high carbon dioxide levels in the blood. It often coexists with obstructive sleep apnea. OHS is classified under ICD-10 code E66.2 and requires urgent medical management including weight loss, respiratory support, and in some cases, bariatric surgery.
Causes and Risk Factors of Obesity
Obesity is the result of multiple factors interacting over time:
- Poor diet: High intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and saturated fats
- Physical inactivity: Sedentary lifestyle and limited movement
- Genetics: Some individuals are predisposed to gain weight more easily
- Psychological factors: Emotional eating due to stress, anxiety, or depression
- Medical conditions: Such as hypothyroidism, PCOS, and certain medications
For example, a sedentary individual consuming excess calories from high-sugar foods daily may see weight gain over time, eventually progressing to obesity if lifestyle changes aren't made.
Statistics on Obesity: A Growing Concern
According to the World Obesity Federation:
- In 2023, over 1 billion people globally were living with obesity
- India is among the top 5 countries with the highest absolute number of adults living with obesity
- Obesity among children aged 5–19 years has more than quadrupled since 1975
The rising trend highlights the need for early diagnosis and effective interventions. School-based awareness programs and personalized plans can help curb the trend before it escalates.
Real Case Study: Reversing Class 2 Obesity with Lifestyle Changes
Rajesh, a 42-year-old software engineer from Bengaluru, was diagnosed with
Obesity Class 2 in 2022. Weighing 108 kg with a BMI of 37, he suffered from high blood pressure and fatigue. With guidance from a certified nutritionist, he followed a customized meal plan, incorporated daily 40-minute walks, and replaced sugary snacks with hydrating options like cucumbers. Over 9 months, Rajesh lost 21 kg and reversed his blood pressure without medication. You can read more about the
health benefits of cucumber in aiding hydration and weight management.
Associated Health Conditions
Untreated obesity can lead to numerous comorbidities:
- Cardiovascular diseases: Increased cholesterol and blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes: Insulin resistance is common in obese individuals
- Respiratory disorders: Including sleep apnea and OHS
- Joint problems: Especially in the knees and hips due to excess load
- Gastrointestinal issues: Including acid reflux and fatty liver disease
- Psychological impact: Depression and social isolation are common
These risks make it essential to implement a comprehensive obesity management plan, especially in older adults or patients with chronic weakness. Read our dedicated
nursing care plan for weakness to understand holistic support strategies.
Diagnosis & Screening
Obesity is diagnosed using:
- BMI measurement
- Waist circumference: Greater than 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women indicates higher risk
- Blood tests: To check cholesterol, blood sugar, thyroid function
- Imaging and sleep studies: Especially if symptoms of OHS or sleep apnea are present
Once confirmed, clinicians assign the appropriate
obesity diagnosis code and formulate a care plan based on the individual's class and comorbidities.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Managing obesity requires a combination of approaches:
- Dietary intervention: Focus on whole foods, vegetables, lean proteins, and hydration
- Physical activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly
- Behavioral therapy: To address emotional and psychological barriers
- Medications: Prescribed in cases where diet and exercise alone don’t suffice
- Bariatric surgery: Considered in Class 3 obesity with health complications
Public health efforts, school-based education, and digital tools like calorie-tracking apps also play a role in promoting long-term health behavior changes.
Conclusion
Obesity is a chronic, multifaceted disease that requires compassionate, evidence-based management. Understanding the types of obesity—from Class 1 to Class 3—and the ICD-10 coding system enables healthcare providers and individuals to respond more effectively. By promoting early screening, personalized nutrition, physical activity, and support for mental health, we can collectively reduce obesity’s impact and improve quality of life across populations.
FAQs About Obesity
What is the ICD-10 code for obesity?
The ICD-10 code for obesity is E66, with subcategories such as E66.0 for excess calories and E66.2 for obesity with hypoventilation.
What are the obesity classes?
Obesity is classified into three types: Class 1 (BMI 30–34.9), Class 2 (BMI 35–39.9), and Class 3 (BMI 40 or above).
How is obesity diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made using BMI, waist circumference, and additional lab tests like blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
What is Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome?
OHS is a condition in severely obese individuals where breathing is inadequate, leading to high carbon dioxide levels. It’s associated with ICD-10 code E66.2.
Can lifestyle changes reverse obesity?
Yes. With proper diet, exercise, and behavioral changes, many individuals have successfully reversed obesity and its related conditions.
Dedicated Support by HealthOK Global
HealthOK Global is here to guide your journey to better health. From personalized nutrition to chronic condition support, our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline is available at
+91-8047190955.
Follow Us on Social Media for More Health Tips!
Stay informed with expert tips on obesity management and wellness. Follow HealthOK Global on
Facebook,
LinkedIn, and
Instagram.