Managing diabetes effectively involves careful dietary planning, especially within the context of traditional Indian cuisine, which is rich in carbohydrates.
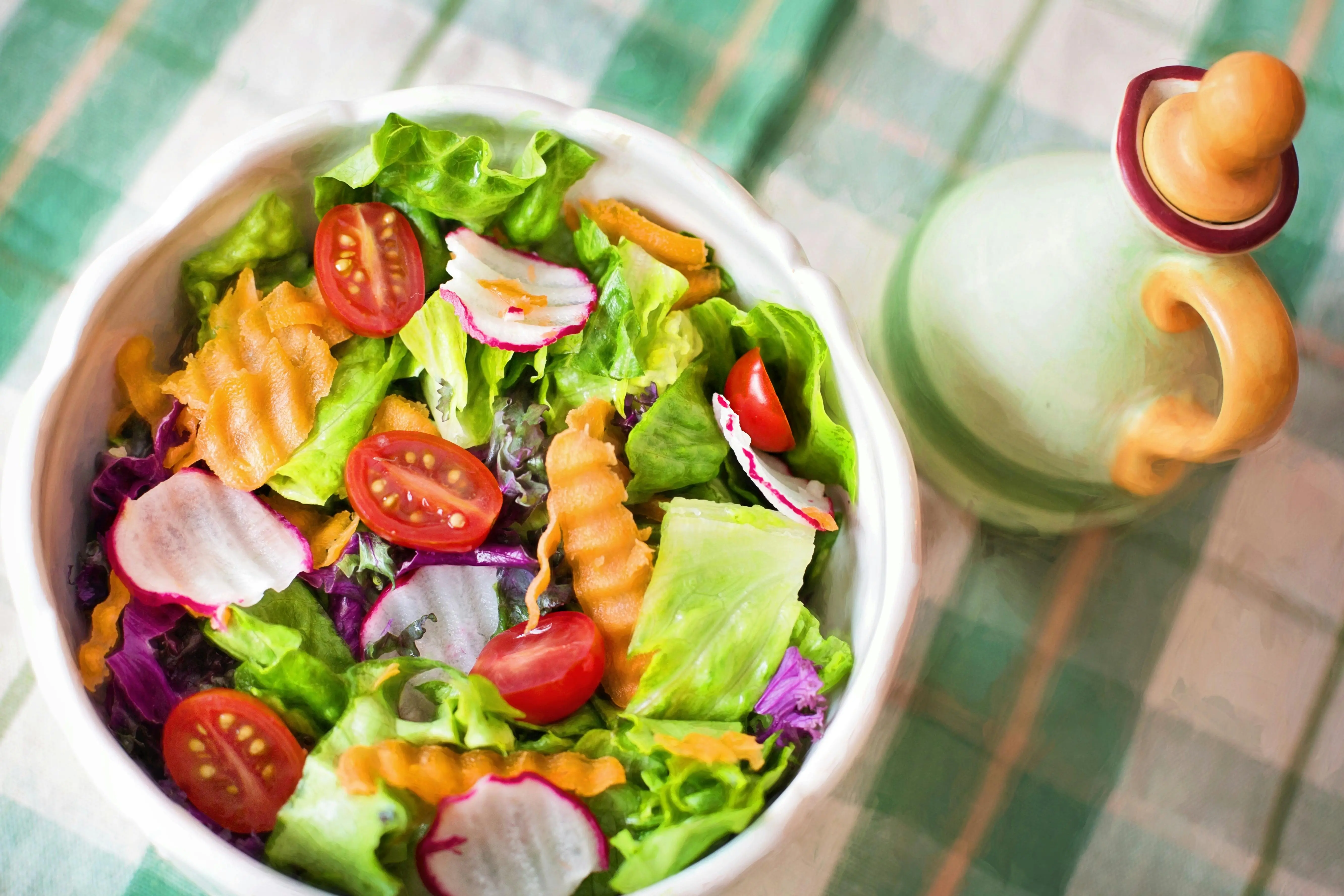
Blog
Indian Diabetic Diet Chart: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively involves careful dietary planning, especially within the context of traditional Indian cuisine, which is rich in carbohydrates. This guide provides a detailed Indian diabetic diet chart to help you maintain stable blood sugar levels while enjoying the flavors of Indian food. For more insights on how diabetes affects sleep and digestion, visit Falling Asleep After Eating: A Diabetes Sign.
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body cannot effectively regulate blood sugar levels. Managing diabetes requires a combination of medication, physical activity, and a carefully monitored diet. For diabetics, it is essential to focus on foods that have a low glycemic index (GI) to prevent blood sugar spikes. Learn more about natural ways to control your blood sugar at Natural Ways to Lower Blood Sugar.
Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. These foods help in maintaining steady blood glucose levels, which is crucial for managing diabetes. Low GI foods include whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits.
Whole grains such as brown rice, millets, and whole wheat are excellent choices as they have a lower glycemic index and help control blood sugar levels.
Yes, diabetics can consume low-GI fruits like apples, pears, guava, and berries. However, high-GI fruits like mangoes and bananas should be consumed in moderation.
Low-fat dairy options such as skim milk, Greek yogurt, and paneer can be included in moderation as part of a balanced diabetic diet.
Eating fiber-rich meals, staying hydrated, and choosing healthy snacks like nuts, seeds, and sprouts can help control cravings effectively.
Cold-pressed oils like mustard oil, olive oil, and coconut oil are recommended as they contain healthy fats that support overall health.
A balanced diet for diabetics includes a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and managing blood sugar levels.
A well-planned meal structure can help regulate blood sugar levels. Here’s a sample meal plan tailored for diabetics in India.
Dietary discipline and mindful eating can significantly impact diabetes management. Here are some key tips to follow.
Managing diabetes effectively requires a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and proper medication. The Indian diabetic diet chart provided in this guide offers nutritious and delicious meal options that help maintain stable blood sugar levels. By following these guidelines and incorporating healthy eating habits into your daily routine, you can effectively manage diabetes and improve your overall health and well-being.
HealthOK Global provides expert insights on nutrition, meal planning, and healthy eating habits. Contact our FREE 24 x 7 Healthcare Helpline at +91-8047190955 for assistance.
Whole grains such as brown rice, millets, and whole wheat are excellent choices as they have a lower glycemic index and help control blood sugar levels.
Yes, diabetics can consume low-GI fruits like apples, pears, guava, and berries. However, high-GI fruits like mangoes and bananas should be consumed in moderation.
Low-fat dairy options such as skim milk, Greek yogurt, and paneer can be included in moderation as part of a balanced diabetic diet.
Eating fiber-rich meals, staying hydrated, and choosing healthy snacks like nuts, seeds, and sprouts can help control cravings effectively.
Cold-pressed oils like mustard oil, olive oil, and coconut oil are recommended as they contain healthy fats that support overall health.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.





