Neurological physiotherapy is a specialized branch of physiotherapy focused on the treatment and rehabilitation of individuals with neurological conditions.
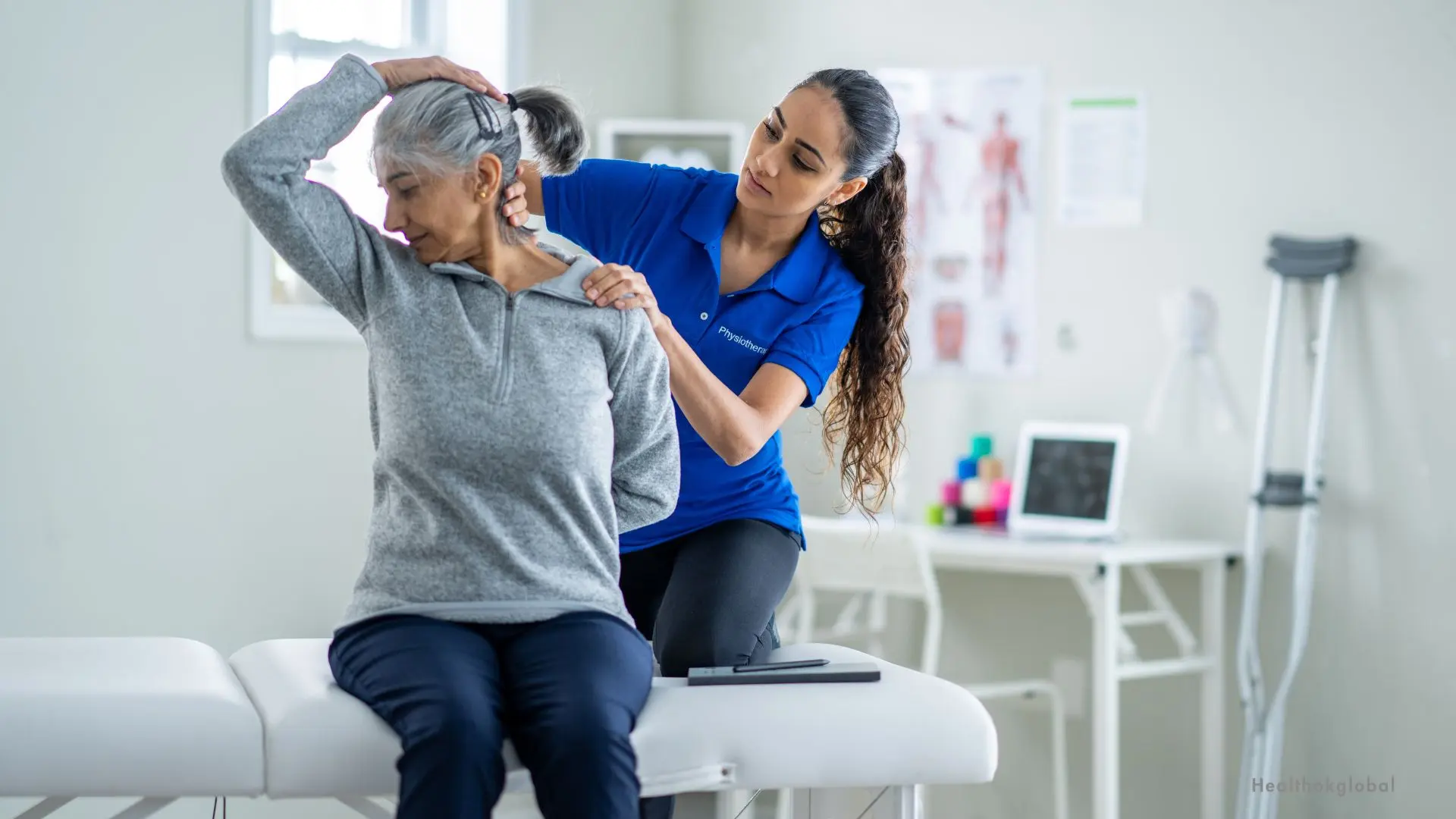
Blog
Neurological Physiotherapy: Enhancing Recovery and Quality of Life
Neurological physiotherapy is a specialized branch of physiotherapy focused on the treatment and rehabilitation of individuals with neurological conditions. These conditions affect the central and peripheral nervous systems, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Neurological physiotherapy aims to improve mobility, function, and quality of life for patients through tailored therapeutic interventions.
Neurological physiotherapy addresses a wide range of conditions, each requiring specific techniques and approaches to manage symptoms and enhance recovery.
Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, resulting from a sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain. Neurological physiotherapy plays a crucial role in stroke rehabilitation by helping patients regain movement and function.
Physiotherapists use exercises to improve strength, coordination, and balance, helping patients relearn how to walk and perform daily activities.
Techniques such as constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) and repetitive task practice are employed to enhance fine motor skills and functional use of the affected limb.
Early intervention helps prevent secondary complications such as joint contractures, muscle atrophy, and pressure sores.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, leading to varying degrees of disability. Neurological physiotherapy helps manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for MS patients.
Physiotherapists develop individualized exercise programs to help manage fatigue, a common symptom of MS, improving endurance and energy levels.
Exercises to improve balance, coordination, and muscle strength are critical in maintaining mobility and independence.
Techniques such as stretching, positioning, and the use of assistive devices help manage muscle spasticity and prevent stiffness.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). Neurological physiotherapy helps improve motor function and quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s.
Physiotherapists use gait training and balance exercises to reduce the risk of falls and improve walking patterns.
Stretching and flexibility exercises help manage rigidity and maintain joint mobility.
Collaboration with speech therapists can address speech and swallowing difficulties associated with Parkinson’s.
Neurological physiotherapy employs a variety of techniques and interventions tailored to the specific needs of each patient. These techniques are designed to improve functional abilities, reduce symptoms, and enhance overall well-being.
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques to mobilize joints, soft tissues, and muscles. It is used to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and enhance circulation.
Techniques to gently mobilize stiff joints, improving flexibility and reducing discomfort.
Massage and myofascial release techniques to alleviate muscle tension and improve tissue health.
Specific stretching exercises to enhance flexibility and prevent contractures.
Exercise therapy is a cornerstone of neurological physiotherapy, focusing on improving strength, coordination, and endurance.
Resistance exercises to build muscle strength and support functional movements.
Activities such as standing on one leg, using balance boards, and coordination drills to improve stability and prevent falls.
Aerobic exercises such as walking, cycling, and swimming to improve cardiovascular health and overall stamina.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections. Neurological physiotherapy leverages this concept to promote recovery and improve function.
Encouraging the use of the affected limb by restricting the unaffected limb, promoting neuroplasticity and functional recovery.
Repetitive practice of functional tasks to enhance neural pathways and improve motor skills.
Using mental visualization of movements to activate the same neural pathways involved in physical execution, supporting rehabilitation.
Neurological physiotherapy offers numerous benefits, significantly impacting the recovery and quality of life of patients with neurological conditions.
Physiotherapy helps patients regain independence in daily activities, enhancing their ability to perform tasks such as dressing, bathing, and walking.
Tailored exercises and interventions improve walking ability, reducing the need for assistive devices and increasing overall mobility.
Improved balance reduces the risk of falls, promoting safety and confidence in movement.
Strength training and endurance exercises enhance physical capacity, allowing patients to engage in activities they enjoy.
Neurological physiotherapy effectively manages pain associated with neurological conditions through various techniques and interventions.
Techniques such as massage and joint mobilization alleviate pain and discomfort, improving patient comfort.
Regular physical activity releases endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, reducing pain perception.
Modalities such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) provide pain relief by modulating nerve activity.
Neurological physiotherapy also provides significant psychological benefits, contributing to overall well-being and mental health.
Physical activity and successful rehabilitation outcomes boost mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Regaining functional abilities and independence enhances self-esteem and confidence.
Improved mobility and independence encourage social participation and interaction, reducing feelings of isolation.
Neurological physiotherapy is a vital component of rehabilitation for individuals with neurological conditions. Through a combination of manual therapy, exercise, and neuroplasticity techniques, physiotherapists help patients improve mobility, manage pain, and enhance their quality of life. The personalized and comprehensive approach of neurological physiotherapy ensures that patients receive the support and care they need to achieve their rehabilitation goals and lead fulfilling lives. Investing in neurological physiotherapy can lead to significant improvements in physical and mental well-being, empowering patients to overcome challenges and achieve greater independence.
Neurological physiotherapy addresses a wide range of conditions, each requiring specific techniques and approaches to manage symptoms and enhance recovery.
Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, resulting from a sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain. Neurological physiotherapy plays a crucial role in stroke rehabilitation by helping patients regain movement and function.
Neurological physiotherapy also provides significant psychological benefits, contributing to overall well-being and mental health.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.