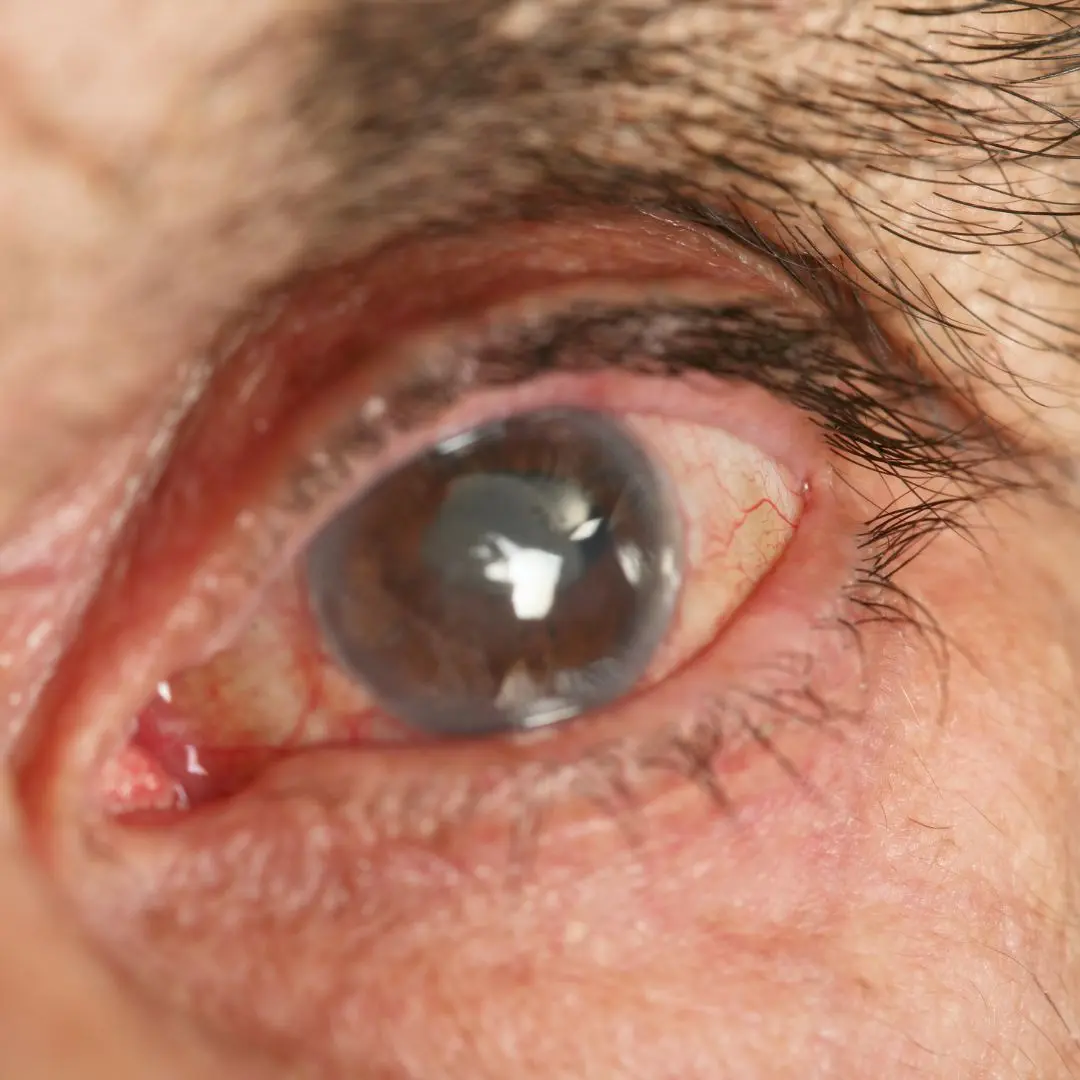
Nuclear cataract is a common age-related eye condition characterized by the clouding of the lens inside the eye.
Blog
Understanding Nuclear Cataract: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Nuclear cataract is a common age-related eye condition characterized by the clouding of the lens inside the eye. It primarily affects the nucleus, or central portion, of the lens, leading to vision changes and visual impairment. Let's delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for nuclear cataract to gain a better understanding of this condition.
The primary cause of nuclear cataract is aging, as the proteins within the lens of the eye undergo structural changes over time, resulting in cloudiness and opacity.
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight over the years may contribute to the development of nuclear cataracts, especially in individuals with prolonged outdoor exposure without adequate eye protection.
Oxidative stress, caused by the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the eye, can damage lens proteins and cellular structures, accelerating the formation of nuclear cataracts.
Nuclear cataracts can cause blurred or cloudy vision, making it difficult to see objects clearly, especially in low light conditions or at night.
People with nuclear cataracts may experience increased sensitivity to glare from bright lights, headlights, or sunlight, leading to discomfort and difficulty driving at night.
Nuclear cataracts can affect color perception, causing colors to appear faded, yellowed, or less vibrant than usual.
Individuals with nuclear cataracts may notice frequent changes in their eyeglass prescription as their vision deteriorates over time.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as wearing sunglasses with UV protection, eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and quitting smoking can help slow the progression of nuclear cataracts and protect overall eye health.
In the early stages of nuclear cataract, prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses may help improve vision and alleviate symptoms such as blurred vision and glare sensitivity.
Cataract surgery is the most effective treatment for advanced nuclear cataracts that significantly impair vision. During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision.
Advanced cataract surgery techniques offer various intraocular lens options, including multifocal lenses and toric lenses, which can correct vision problems such as presbyopia and astigmatism in addition to treating cataracts.
Regular eye examinations are essential for monitoring the progression of nuclear cataracts and detecting any changes in vision early on. Early intervention can help prevent vision loss and improve treatment outcomes.
Using bright, adequate lighting when reading or performing close-up tasks can help compensate for vision changes caused by nuclear cataracts and reduce eyestrain.
Individuals with nuclear cataracts may find it challenging to drive at night due to glare sensitivity and reduced contrast sensitivity. Avoiding nighttime driving or using alternative transportation methods can help ensure safety on the road.
Nuclear cataract is a common age-related eye condition characterized by the clouding of the lens nucleus, leading to vision changes and visual impairment. While nuclear cataracts cannot be reversed, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for nuclear cataract, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their vision and maintain eye health as they age. If you experience symptoms of nuclear cataract, consult with an eye care professional for evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
The primary cause of nuclear cataract is aging, as the proteins within the lens of the eye undergo structural changes over time, resulting in cloudiness and opacity.
Nuclear cataracts can cause blurred or cloudy vision, making it difficult to see objects clearly, especially in low light conditions or at night.
This section covers Managing Nuclear Cataract Symptoms in detail.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.