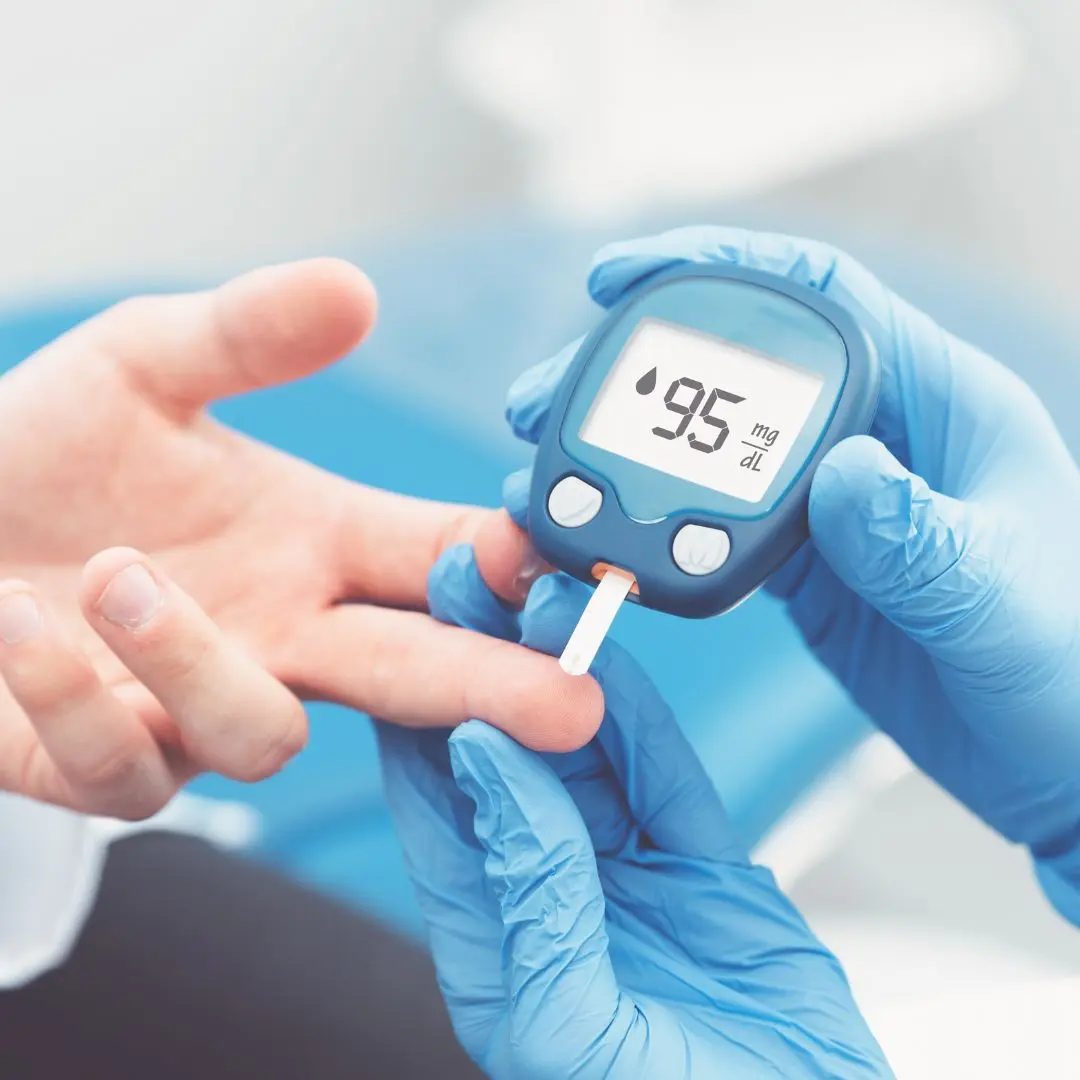
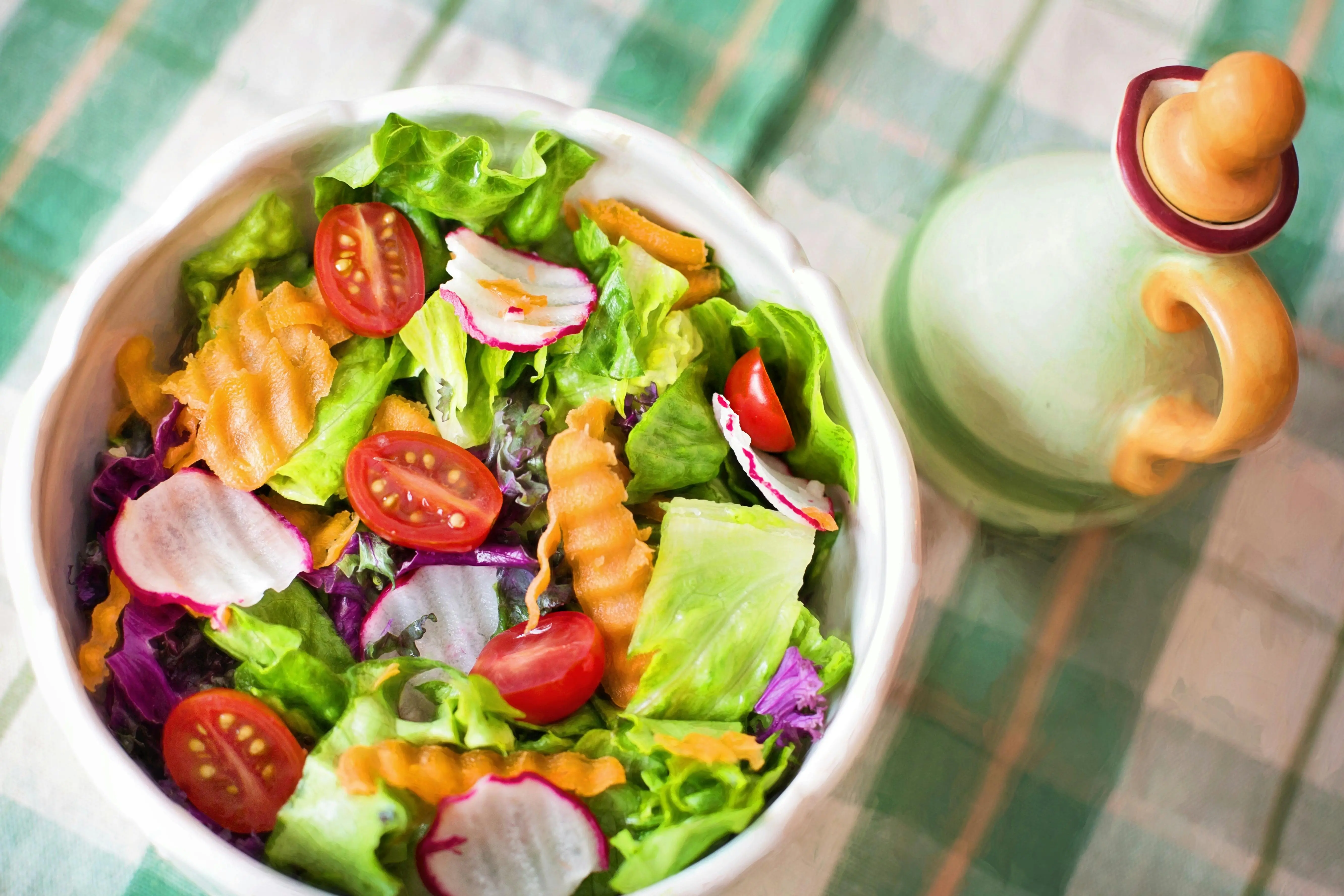Living with prediabetes means that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.

Blog
The Ultimate Guide to a Prediabetes Diet Plan
Living with prediabetes means that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It's a critical moment for intervention through lifestyle changes, primarily focusing on diet, to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. This guide offers a deep dive into a prediabetes diet plan, detailing the crucial components of what to eat and avoid for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Prediabetes is a condition affecting millions globally, acting as a precursor to type 2 diabetes. It's characterized by slightly elevated blood sugar levels, which are a result of insulin resistance or a deficiency in insulin production. Diet plays a pivotal role in managing prediabetes because what you eat directly impacts your blood sugar levels. Adopting a diet that stabilizes these levels can help reverse the condition and prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
A prediabetes diet is built on the principle of balance—balancing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to support stable blood sugar levels and overall health. Here's how you can achieve this balance:
Eating whole, nutrient-rich foods is essential for managing prediabetes. This includes incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet. These foods provide your body with the necessary fiber, vitamins, and minerals to support blood sugar control and improve metabolic health.
Carbohydrates have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, making it important to choose them wisely. Opt for complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, over refined carbs and sugary foods. Complex carbs are digested more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels rather than sharp spikes.
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet can help slow the absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid increases in blood sugar. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon. These fats not only support blood sugar control but also contribute to heart health, which is crucial for individuals with prediabetes.
Lean proteins are an essential component of a prediabetes diet. They provide energy without the extra fat and help keep you feeling full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Good sources of lean protein include poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes.
Proper hydration is vital for blood sugar control. Drinking adequate amounts of water throughout the day helps maintain normal blood sugar levels and supports overall metabolic function. Aim to drink water primarily, and limit sugary drinks and high-caffeine beverages.
Your diet should primarily consist of foods that support healthy blood sugar levels. This includes whole grains like quinoa and brown rice; vegetables, particularly leafy greens and non-starchy varieties; fruits, such as berries and apples, in moderation; lean protein sources, including fish and poultry; and healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
To manage prediabetes effectively, certain foods should be limited or avoided. These include refined carbohydrates found in white bread and pasta, sugary snacks and beverages, high-fat meats, and trans fats commonly found in processed foods. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
A balanced day might start with oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a handful of walnuts for breakfast. Lunch could be a grilled chicken salad with a variety of vegetables, dressed with olive oil and lemon juice. For snacks, consider sliced apples with almond butter. Dinner might feature baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli. For a treat, Greek yogurt with a sprinkle of cinnamon can satisfy sweet cravings without spiking your blood sugar.
Managing prediabetes extends beyond diet alone. Regular exercise, weight management, stress reduction, and regular health check-ups play a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels and preventing the progression to type 2 diabetes. A holistic approach that incorporates these lifestyle changes alongside a balanced diet offers the best chance for reversing prediabetes.
Prediabetes is a condition affecting millions globally, acting as a precursor to type 2 diabetes. It's characterized by slightly elevated blood sugar levels, which are a result of insulin resistance or a deficiency in insulin production. Diet plays a pivotal role in managing prediabetes because what you eat directly impacts your blood sugar levels. Adopting a diet that stabilizes these levels can help reverse the condition and prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
A prediabetes diet is built on the principle of balance—balancing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to support stable blood sugar levels and overall health. Here's how you can achieve this balance:
Your diet should primarily consist of foods that support healthy blood sugar levels. This includes whole grains like quinoa and brown rice; vegetables, particularly leafy greens and non-starchy varieties; fruits, such as berries and apples, in moderation; lean protein sources, including fish and poultry; and healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Need Personalized Health Guidance?
Get expert advice tailored to your specific health needs from our qualified healthcare professionals.